5-[(3,5-Dichloro-anilino)meth-yl]-N-(3,5-dichloro-phen-yl)-6-methyl-2-phenyl-pyrimidin-4-amine
- PMID: 23476235
- PMCID: PMC3588999
- DOI: 10.1107/S160053681204665X
5-[(3,5-Dichloro-anilino)meth-yl]-N-(3,5-dichloro-phen-yl)-6-methyl-2-phenyl-pyrimidin-4-amine
Abstract
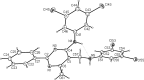
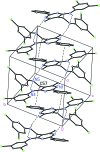
In the title compound, C24H18Cl4N4, the pyrimidine ring makes dihedral angles of 19.1 (2), 4.1 (2) and 67.5 (2)°, respectively, with phenyl and two benzene rings, and the mol-ecular conformation is stabilized by an intra-molecular N-H⋯N hydrogen bond closing a six-membered ring with an S(6) motif. In the crystal, a pair of inter-molecular N-H⋯N hydrogen bonds connect two mol-ecules, forming inversion dimers with R2(2)(12) motifs. C-H⋯π inter-actions links the dimers into a chain running along the a-axis direction. There are also π-π stacking inter-actions [centroid-centroid distance = 3.666 (4) Å] between the benzene rings of adjacent chains.
Figures
References
-
- Cieplik, J., Pluta, J., Bryndal, I. & Lis, T. (2006). Acta Cryst. C62, o259–o261. - PubMed
-
- Cieplik, J., Pluta, J. & Gubrynowicz, O. (2003). Boll. Chim. Farm. 142, 146–150. - PubMed
-
- Cieplik, J., Raginia, M., Pluta, J., Gubrynowicz, O., Bryndal, I. & Lis, T. (2008). Acta Pol. Pharm. Drug Res. 65, 427–434. - PubMed
-
- Oxford Diffraction (2007). CrysAlis CCD and CrysAlis RED. Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Abington, England.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
