Proteases from Entamoeba spp. and Pathogenic Free-Living Amoebae as Virulence Factors
- PMID: 23476670
- PMCID: PMC3582061
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/890603
Proteases from Entamoeba spp. and Pathogenic Free-Living Amoebae as Virulence Factors
Abstract
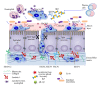
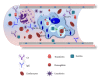
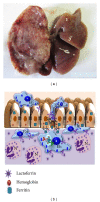
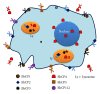
The standard reference for pathogenic and nonpathogenic amoebae is the human parasite Entamoeba histolytica; a direct correlation between virulence and protease expression has been demonstrated for this amoeba. Traditionally, proteases are considered virulence factors, including those that produce cytopathic effects in the host or that have been implicated in manipulating the immune response. Here, we expand the scope to other amoebae, including less-pathogenic Entamoeba species and highly pathogenic free-living amoebae. In this paper, proteases that affect mucin, extracellular matrix, immune system components, and diverse tissues and cells are included, based on studies in amoebic cultures and animal models. We also include proteases used by amoebae to degrade iron-containing proteins because iron scavenger capacity is currently considered a virulence factor for pathogens. In addition, proteases that have a role in adhesion and encystation, which are essential for establishing and transmitting infection, are discussed. The study of proteases and their specific inhibitors is relevant to the search for new therapeutic targets and to increase the power of drugs used to treat the diseases caused by these complex microorganisms.
Figures
References
-
- Pawlowski J, Burki F. Untangling the phylogeny of amoeboid protists. Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology. 2009;56(1):16–25. - PubMed
-
- Jackson TFHG. Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba dispar are distinct species; clinical, epidemiological and serological evidence. International Journal for Parasitology. 1998;28(1):181–186. - PubMed
-
- Tengku SA, Norhayati M. Public health and clinical importance of amoebiasis in Malaysia: a review. Tropical Biomedicine. 2011;28(2):194–222. - PubMed
-
- Romeralo M, Escalante R, Baldauf SL. Evolution and diversity of dictyostelid social amoebae. Protist. 2012;163(3):327–343. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

