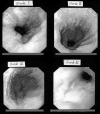
The effect of Helicobacter pylori on gastroesophageal reflux disease
- PMID: 23477175
- PMCID: PMC3481226
- DOI: 10.4293/108680812x13427982376860
The effect of Helicobacter pylori on gastroesophageal reflux disease
Abstract
Background and objectives: Helicobacter pylori infection represents one of the most common and medically prominent infections worldwide. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) has a multifactorial etiology. The nature of the relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection (HP) and reflux esophagitis is still not clear. This study is designed to find the influence of HP on GERD.
Patients and methods: The study was conducted retrospectively at Sakarya Newcity Hospital between January 2006 and January 2009. Data were collected on patient's age, sex, weight, the grade of GERD and the severity of HP.
Results: There were 1,307 women and 1,135 men in this review with a mean age of 39,54 (range, 17 to 70) years. Helicobacter pylori positive (1 to 3 severity) was frequently seen in patients with GERD. A statistically significant relationship was found between HP positivity and the grade of GERD. The Helicobacter pylori infection (1 to 3 severity) was found in 1,437 (82.5%) of patients with GERD in our series.
Conclusions: Controversy still exists about the association between GERD and HP infection. Based on our findings, significant evidence suggests the potential role of HP infection in the development of GERD. Also, the current data provide sufficient evidence to define the relationship between GERD and HP infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Helicobacter pylori and gastroesophageal reflux disease.World J Surg Oncol. 2008 Jul 5;6:74. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-6-74. World J Surg Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18601740 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of patients with erosive and nonerosive GERD in high-Helicobacter-pylori prevalence region.Dis Esophagus. 2004;17(3):223-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2050.2004.00412.x. Dis Esophagus. 2004. PMID: 15361095
-
Association of Helicobacter pylori infection with gastroesophageal reflux disease.J Int Med Res. 2019 Feb;47(2):748-753. doi: 10.1177/0300060518809871. Epub 2018 Nov 19. J Int Med Res. 2019. PMID: 30453813 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between Helicobacter pylori and gastroesophageal reflux disease.Esophagus. 2019 Jan;16(1):52-62. doi: 10.1007/s10388-018-0637-5. Epub 2018 Aug 27. Esophagus. 2019. PMID: 30151653 Review.
-
Helicobacter pylori and gastroesophageal reflux disease.Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1999 Dec;28(4):971-85, viii. doi: 10.1016/s0889-8553(05)70100-x. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1999. PMID: 10695012 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on reflux esophagitis therapy: a multi-center randomized control study.Chin Med J (Engl). 2015 Apr 20;128(8):995-9. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.155049. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015. PMID: 25881589 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Issues and controversies in esophageal inlet patch.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Aug 14;25(30):4061-4073. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i30.4061. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31435164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Not Every Dyspepsia Is Related to Helicobacter pylori-A Case of Esophageal Inlet Patch in a Female Teenager.Children (Basel). 2023 Jan 28;10(2):229. doi: 10.3390/children10020229. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36832358 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of the Microbiome Metagenomics and Epigenomics on Gastric Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 9;23(22):13750. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213750. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identifying the Demographic, Clinical, and Endoscopic Findings of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Patients With Helicobacter pylori Infection at King Abdulaziz University Hospital, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.Cureus. 2022 Jul 4;14(7):e26542. doi: 10.7759/cureus.26542. eCollection 2022 Jul. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35936155 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vaezi MF, Swoger J. Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in the elderly. In: Granderath FA, Pointner KT, eds. Gastro-oesophageal Reflux Disease. Wien: Springer; 2006;23–45
-
- Chourasia D, Ghoshal UC. Pathogenesis of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: what role do Helicobacter pylori and host genetic factors play? Trop Gastroenterol. 2008;29(1):13–19 - PubMed
-
- Kwon JH, Chung IS, Son HS, et al. The relationship of gastrin, pepsinogen, and Helicobacter pylori in erosive reflux esophagitis. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2008;51(3):159–166 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous