Phase III randomized study of rituximab/carmustine, etoposide, cytarabine, and melphalan (BEAM) compared with iodine-131 tositumomab/BEAM with autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation for relapsed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: results from the BMT CTN 0401 trial
- PMID: 23478060
- PMCID: PMC3635682
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2012.45.9453
Phase III randomized study of rituximab/carmustine, etoposide, cytarabine, and melphalan (BEAM) compared with iodine-131 tositumomab/BEAM with autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation for relapsed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: results from the BMT CTN 0401 trial
Abstract
Purpose: This clinical trial evaluated standard-dose radioimmunotherapy with a chemotherapy-based transplantation regimen followed by autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation versus rituximab with the same regimen in patients with relapsed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Patients and methods: Patients with chemotherapy-sensitive persistent or relapsed DLBCL were randomly assigned to receive iodine-131 tositumomab (dosimetric dose of 5 mCi on day -19 and therapeutic dose of 0.75 Gy on day -12), carmustine 300 mg/m(2) (day -6), etoposide 100 mg/m(2) twice daily (days -5 to -2), cytarabine 100 mg/m(2) twice daily (days -5 to -2), and melphalan 140 mg/m(2) (day -1; B-BEAM) or rituximab 375 mg/m(2) on days -19 and -12 and the same chemotherapy regimen (R-BEAM).
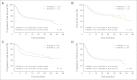
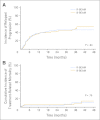
Results: Two hundred twenty-four patients were enrolled, with 113 patients randomly assigned to R-BEAM and 111 patients assigned to B-BEAM. Two-year progression-free survival (PFS) rates, the primary end point, were 48.6% (95% CI, 38.6% to 57.8%) for R-BEAM and 47.9% (95% CI, 38.2% to 57%; P = .94) for B-BEAM, and the 2-year overall survival (OS) rates were 65.6% (95% CI, 55.3% to 74.1%) for R-BEAM and 61% (95% CI, 50.9% to 69.9%; P = .38) for B-BEAM. The 100-day treatment-related mortality rates were 4.1% (95% CI, 0.2% to 8.0%) for R-BEAM and 4.9% (95% CI, 0.8% to 9.0%; P = .97) for B-BEAM. The maximum mucositis score was higher in the B-BEAM arm (0.72) compared with the R-BEAM arm (0.31; P < .001).
Conclusion: The B-BEAM and R-BEAM regimens produced similar 2-year PFS and OS rates for patients with chemotherapy-sensitive relapsed DLBCL. No differences in toxicities other than mucositis were noted.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00329030.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Philip T, Guglielmi C, Hagenbeek A, et al. Autologous bone marrow transplantation as compared with salvage chemotherapy in relapses of chemotherapy-sensitive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:1540–1545. - PubMed
-
- Vose JM, Zhang MJ, Rowlings PA, et al. Autologous transplantation for diffuse aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma in patients never achieving remission: A report from the autologous blood and marrow transplant registry. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:406–413. - PubMed
-
- Nademanee A, Molina A, Dagis A, et al. Autologous stem-cell transplantation for poor-risk and relapsed intermediate- and high-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Clin Lymphoma. 2000;1:46–54. - PubMed
-
- Schmitz N, Buske C, Gisselbrecht C. Autologous stem cell transplantation in lymphoma. Semin Hematol. 2007;44:234–245. - PubMed
-
- Caballero MD, Rubio V, Rifon J, et al. BEAM chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell support in lymphoma patients: Analysis of efficacy, toxicity and prognostic factors. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1997;20:451–458. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U10 HL069294/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HL069286/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL069290/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL069301/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL069330/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL069249/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL069310/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL069294/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016520/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL069348/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA076518/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL069286/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL069294/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

