ER structure and function
- PMID: 23478217
- PMCID: PMC5614462
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceb.2013.02.006
ER structure and function
Abstract
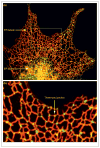
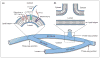
The ER forms a contiguous structure of interconnected sheets and tubules that spreads from the nuclear envelope to the cell cortex. Through its attachment to the cytoskeleton, the ER undergoes dynamic rearrangements, such as tubule extension and movement. ER shaping proteins (reticulons and DP1/Yop1p) play key roles in generating and maintaining the unique reticular morphology of the ER. Atlastin and its yeast homologue, Sey1p, mediate homotypic ER membrane fusion, which leads to the formation of new three-way junctions within the polygonal network. At these junctions, the Lunapark protein, Lnp1p, works in conjunction with the reticulons, DP1/Yop1p, and in antagonism to atlastin/Sey1p to maintain the network in a dynamic equilibrium. Defects in ER morphology have been linked to certain neurological disorders.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Baumann O, Walz B. Endoplasmic reticulum of animal cells and its organization into structural and functional domains. Int Rev Cytol. 2001;205:149–214. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe R, Riezman H. Differential ER exit in yeast and mammalian cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004;16:350–355. - PubMed
-
- Du Y, Ferro-Novick S, Novick P. Dynamics and inheritance of the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Sci. 2004;117:2871–2878. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

