Genetically engineered mouse models of PI3K signaling in breast cancer
- PMID: 23478237
- PMCID: PMC5528412
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molonc.2013.02.003
Genetically engineered mouse models of PI3K signaling in breast cancer
Abstract
Breast cancer is the most common type of cancer in women. A substantial fraction of breast cancers have acquired mutations that lead to activation of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) signaling pathway, which plays a central role in cellular processes that are essential in cancer, such as cell survival, growth, division and motility. Oncogenic mutations in the PI3K pathway generally involve either activating mutation of the gene encoding PI3K (PIK3CA) or AKT (AKT1), or loss or reduced expression of PTEN. Several kinases involved in PI3K signaling are being explored as a therapeutic targets for pharmacological inhibition. Despite the availability of a range of inhibitors, acquired resistance may limit the efficacy of single-agent therapy. In this review we discuss the role of PI3K pathway mutations in human breast cancer and relevant genetically engineered mouse models (GEMMs), with special attention to the role of PI3K signaling in oncogenesis, in therapeutic response, and in resistance to therapy. Several sophisticated GEMMs have revealed the cause-and-effect relationships between PI3K pathway mutations and mammary oncogenesis. These GEMMs enable us to study the biology of tumors induced by activated PI3K signaling, as well as preclinical response and resistance to PI3K pathway inhibitors.
Copyright © 2013 Federation of European Biochemical Societies. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
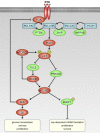
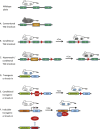
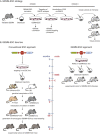
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of constitutively activated phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT pathway enhances antitumor activity of chemotherapeutic agents in breast cancer susceptibility gene 1-defective breast cancer cells.Mol Carcinog. 2013 Sep;52(9):667-75. doi: 10.1002/mc.21905. Epub 2012 Apr 4. Mol Carcinog. 2013. PMID: 22488590 Free PMC article.
-
Combination Therapy Approach to Overcome the Resistance to PI3K Pathway Inhibitors in Gynecological Cancers.Cells. 2024 Jun 19;13(12):1064. doi: 10.3390/cells13121064. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38920692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preclinical modeling of combined phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase inhibition with endocrine therapy for estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2011 Mar 1;13(2):R21. doi: 10.1186/bcr2833. Breast Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21362200 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical Efficacy of Ron Kinase Inhibitors Alone and in Combination with PI3K Inhibitors for Treatment of sfRon-Expressing Breast Cancer Patient-Derived Xenografts.Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Dec 15;21(24):5588-600. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-3283. Epub 2015 Aug 19. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26289070 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of PI3K inhibitors in advanced breast cancer.Ann Oncol. 2019 Dec 1;30(Suppl_10):x12-x20. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdz381. Ann Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31859349 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multiplexed imaging reveals heterogeneity of PI3K/MAPK network signaling in breast lesions of known PIK3CA genotype.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016 Oct;159(3):575-83. doi: 10.1007/s10549-016-3962-1. Epub 2016 Aug 31. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016. PMID: 27581127 Free PMC article.
-
Genetically engineered ERα-positive breast cancer mouse models.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2014 May 6;21(3):R195-208. doi: 10.1530/ERC-13-0512. Print 2014 Jun. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24481326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling role of oncogenic signalling pathways in complicating breast cancer.Biomedicine (Taipei). 2025 Mar 1;15(1):13-21. doi: 10.37796/2211-8039.1640. eCollection 2025. Biomedicine (Taipei). 2025. PMID: 40176859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mammary gland tumor promotion by chronic administration of IGF1 and the insulin analogue AspB10 in the p53R270H/⁺WAPCre mouse model.Breast Cancer Res. 2015 Feb 18;17(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s13058-015-0518-y. Breast Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25848982 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutively activated PI3K accelerates tumor initiation and modifies histopathology of breast cancer.Oncogenesis. 2016 Oct 31;5(10):e267. doi: 10.1038/oncsis.2016.65. Oncogenesis. 2016. PMID: 27797363 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ackler, S. , Ahmad, S. , Tobias, C. , Johnson, M.D. , Glazer, R.I. , 2002. Delayed mammary gland involution in MMTV-AKT1 transgenic mice. Oncogene 21, 198–206. - PubMed
-
- Adams, J.R. , Xu, K. , Liu, J.C. , Agamez, N.M.R. , Loch, A.J. , Wong, R.G. , Wang, W. , Wright, K.L. , Lane, T.F. , Zacksenhaus, E. , Egan, S.E. , 2011. Cooperation between Pik3ca and p53 mutations in mouse mammary tumor formation. Cancer Res. 71, 2706–2717. - PubMed
-
- Alimonti, A. , Carracedo, A. , Clohessy, J.G. , Trotman, L.C. , Nardella, C. , Egia, A. , Salmena, L. , Sampieri, K. , Haveman, W.J. , Brogi, E. , Richardson, A.L. , Zhang, J. , Pandolfi, P.P. , 2010. Subtle variations in Pten dose determine cancer susceptibility. Nat. Genet. 42, 454–458. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andre, F. , Campone, M. , O'Regan, R. , Manlius, C. , Massacesi, C. , Sahmoud, T. , Mukhopadhyay, P. , Soria, J.-C. , Naughton, M. , Hurvitz, S.A. , 2010. Phase I study of everolimus plus weekly paclitaxel and trastuzumab in patients with metastatic breast cancer pretreated with trastuzumab. J. Clin. Oncol. 28, 5110–5115. - PubMed
-
- Bachelot, T. , Bourgier, C. , Cropet, C. , Guastalla, J.-P. , Ferrero, J.-M. , Leger-Falandry, C. , Soulie, P. , Eymard, J.-C. , Debled, M. , Spaeth, D. , Legouffe, E. , Delozier, T. , El Kouri, C. , Chidiac, J. , 2011. TAMRAD: a GINECO randomized phase II trial of everolimus in combination with tamoxifen versus tamoxifen alone in patients (pts) with hormone-receptor positive, HER2 negative metastatic breast cancer (MBC) with prior exposure to aromatase inhibitors (AI). Cancer Res. 70, Abstract S1–6
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

