STING recognition of cytoplasmic DNA instigates cellular defense
- PMID: 23478444
- PMCID: PMC3881179
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.01.039
STING recognition of cytoplasmic DNA instigates cellular defense
Abstract
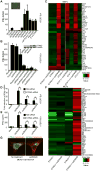
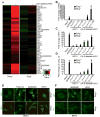
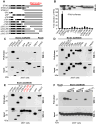
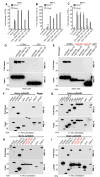
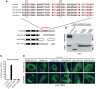
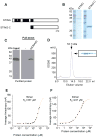
How the cell recognizes cytosolic DNA including DNA-based microbes to trigger host-defense-related gene activation remains to be fully resolved. Here, we demonstrate that STING (stimulator of interferon genes), an endoplasmic reticulum translocon-associated transmembrane protein, acts to detect cytoplasmic DNA species. STING homodimers were able to complex with self- (apoptotic, necrotic) or pathogen-related ssDNA and dsDNA and were indispensible for HSV-1-mediated transcriptional activation of a wide array of innate immune and proinflammatory genes in addition to type I IFN. Our data indicate that STING instigates cytoplasmic DNA-mediated cellular defense gene transcription and facilitates adoptive responses that are required for protection of the host. In contrast, chronic STING activation may manifest inflammatory responses and possibly autoimmune disease triggered by self-DNA.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
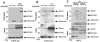
Comment in
-
How do cells sense foreign DNA? A new outlook on the function of STING.Mol Cell. 2013 Apr 11;50(1):1-2. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.03.024. Mol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23582257
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

