Chondroitin sulfate, hyaluronic acid and chitin/chitosan production using marine waste sources: characteristics, applications and eco-friendly processes: a review
- PMID: 23478485
- PMCID: PMC3705368
- DOI: 10.3390/md11030747
Chondroitin sulfate, hyaluronic acid and chitin/chitosan production using marine waste sources: characteristics, applications and eco-friendly processes: a review
Abstract
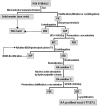
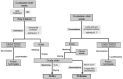
In the last decade, an increasing number of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), chitin and chitosan applications have been reported. Their commercial demands have been extended to different markets, such as cosmetics, medicine, biotechnology, food and textiles. Marine wastes from fisheries and aquaculture are susceptible sources for polymers but optimized processes for their recovery and production must be developed to satisfy such necessities. In the present work, we have reviewed different alternatives reported in the literature to produce and purify chondroitin sulfate (CS), hyaluronic acid (HA) and chitin/chitosan (CH/CHs) with the aim of proposing environmentally friendly processes by combination of various microbial, chemical, enzymatic and membranes strategies and technologies.
Figures


References
-
- Food and Agriculture Organization. Estadísticas de Pesca: Captura y Desembarques. FAO; Roma, Italy: 2004.
-
- Gildberg A. Recovery of proteinases and protein hydrolysates from fish viscera. Bioresour. Technol. 1992;39:271–276. doi: 10.1016/0960-8524(92)90216-K. - DOI
-
- Blanco M., Sotelo C.G., Chapela M.J., Pérez-Martín R.I. Towards sustainable and efficient use of fishery resources: Present and future trends. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2007;18:29–36. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2006.07.015. - DOI
-
- European Community. On a European Community plan of action for the conservation and management of sharks. [(accessed on 10 November 2012)]. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/fisheries/marine_species/wild_species/sharks/index_e....
-
- Arvanitoyannis I.S., Kassaveti A. Fish industry waste: Treatments, environmental impacts, current and potential uses. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2008;43:726–745. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.2006.01513.x. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

