Malaria pigment crystals as magnetic micro-rotors: key for high-sensitivity diagnosis
- PMID: 23478535
- PMCID: PMC3594758
- DOI: 10.1038/srep01431
Malaria pigment crystals as magnetic micro-rotors: key for high-sensitivity diagnosis
Abstract
The need to develop new methods for the high-sensitivity diagnosis of malaria has initiated a global activity in medical and interdisciplinary sciences. Most of the diverse variety of emerging techniques are based on research-grade instruments, sophisticated reagent-based assays or rely on expertise. Here, we suggest an alternative optical methodology with an easy-to-use and cost-effective instrumentation based on unique properties of malaria pigment reported previously and determined quantitatively in the present study. Malaria pigment, also called hemozoin, is an insoluble microcrystalline form of heme. These crystallites show remarkable magnetic and optical anisotropy distinctly from any other components of blood. As a consequence, they can simultaneously act as magnetically driven micro-rotors and spinning polarizers in suspensions. These properties can gain importance not only in malaria diagnosis and therapies, where hemozoin is considered as drug target or immune modulator, but also in the magnetic manipulation of cells and tissues on the microscopic scale.
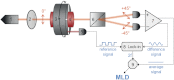
Figures
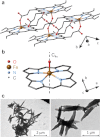

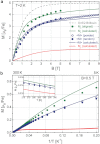
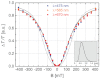


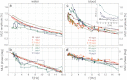
References
-
- World malaria report 2011, December 13, 2011. (http://www.who.int/malaria).
-
- Greenwood B. M., Bojang K., Whitty C. J. & Targett G. A. Malaria. Lancet 365, 1487–1498 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Bell D., Wongsrichanalai C. & Barnwell J. W. Ensuring quality and access for malaria diagnosis: how can it be achieved? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 4, 682–695 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

