Effect of horizontal rectus surgery on clinical and paraclinical indices in congenital nystagmus
- PMID: 23479515
- PMCID: PMC3589220
Effect of horizontal rectus surgery on clinical and paraclinical indices in congenital nystagmus
Abstract
Purpose: To determine the effect of horizontal rectus muscle surgery on visual acuity, head posture and electronystagmographic indices in patients with congenital nystagmus.
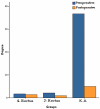
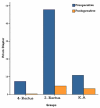
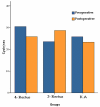
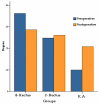
Methods: This prospective comparative case series was conducted on 58 patients with congenital nystagmus over a period of three years. Patients were divided into three groups: the first group (29 cases) had head posture less than 20°, binocular visual acuity (BOVA) less than 20/30 and tropia less than 30Δ and underwent large recession of all four horizontal rectus muscles; the second group (23 cases) had head posture less than 20°, BOVA< 20/30 and tropia more than 30Δ who underwent large recession of two horizontal rectus muscles; and the third group (6 cases) had head posture more than 20° with any BOVA or tropia who underwent Kestenbaum-Anderson surgery.
Results: Mean age of the patients was 18.7±9.1 years and mean follow-up period was 17.5±7.4 months. Visual acuity improved in all three study groups and was statistically significant in the 2-rectus group (P<0.001). The speed and amplitude of nystagmus waves decreased in all groups which was statistically significant in the 4-rectus group (P values, 0.02 and 0.04, respectively). A small myopic shift was seen in the 2-rectus and 4-rectus groups and a small hyperopic shift was found in the Kestenbaum-Anderson group. Statistically significant improvement was achieved in eye deviation in the 2-rectus group and in head posture in the Kestenbaum-Anderson group (P<0.001).
Conclusion: Horizontal recti surgery in congenital nystagmus can improve visual acuity, ocular deviation and abnormal head posture, which is particularly marked with 2-rectus recession. Electronystagmographic indices improve especially with 4-rectus recession.
Figures

References
-
- Repka MX. Nystagmus: clinical evaluation and surgical management. In: Rosenbaum AL, Santiago AP, editors. Clinical strabismus management, principle and surgical techniques. 1st ed. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Co.; 1999. pp. 404–420.
-
- Zubcov AA, Stark N, Weber A, Wizov SS, Reincke RD. Improvement of visual acuity after surgery for nystagmus. Ophthalmology. 1993;100:1488–1497. - PubMed
-
- Helveston EM, Ellis FD, Plager DA. Large recessions of the horizontal recti for treatment of nystagmus. Ophthalmology. 1991;98:1302–1305. - PubMed
-
- Von Noordon GK, Sprunger DT. Large recti muscle recessions for the treatment of congenital nystagmus. Arch Ophthalmol. 1991;109:221–224. - PubMed
-
- Fioretto M, Burtolo C, Fava GP. New surgical methods for nystagmus without null point. Ophthalmology. 1991;203:180–183. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
