Olfactory assessment using the NIH Toolbox
- PMID: 23479541
- PMCID: PMC3662337
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182872eb4
Olfactory assessment using the NIH Toolbox
Abstract
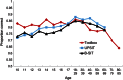
The human olfactory system provides us with information about our environment that is critical to our physical and psychological well-being. Individuals can vary widely in their ability to detect, recognize, and identify odors, but still be within the range of normal function. Although several standardized tests of odor identification are available, few specifically address the issues in testing very young children, most of whom are likely to be unfamiliar with many of the odor stimuli used in adult tests and have limited ability to read and identify labels to select among choices. Based on the format of the San Diego Odor Identification Test and the delivery system of the University of Pennsylvania Smell Identification Test, we developed 2 versions of an odor identification test using standardized odor stimuli in a scratch-and-sniff format in which participants match 5 (children) or 9 (adults) odors to pictures representing the odor source. Results from normative testing and validation showed that for most participants, the test could be completed in 5 minutes or less and that the poorer performance among the youngest children and the elderly was consistent with data from tests with larger numbers of items. Expanding on the pediatric version of the test with adult-specific and public health-relevant odors increased the ecological validity of the test and facilitated comparisons of intraindividual performance across developmental stages.
Figures
References
-
- Murthy V. Olfactory maps in the brain. Ann Rev Neurosci 2011;34:233–258 - PubMed
-
- Ruijschop RMAJ, Boelrijk AEM, de Graaf C, Westerterp-Plantenga MS. Retronasal aroma release and satiation: a review. J Agric Food Chem 2009;57:9888–9894 - PubMed
-
- Doty RL. The olfactory system and its disorders. Semin Neurol 2009;29:74–81 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 MH063381/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC 03275/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG004085/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD028138/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- NIH K01 MH090548-01/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG04085-24/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH 63381/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG041795/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH 59852/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059852/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- DC02064-14/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DC 006760/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC002064/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources