DNA methylation by CcrM activates the transcription of two genes required for the division of Caulobacter crescentus
- PMID: 23480529
- PMCID: PMC3708114
- DOI: 10.1111/mmi.12180
DNA methylation by CcrM activates the transcription of two genes required for the division of Caulobacter crescentus
Abstract
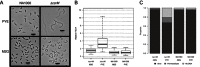
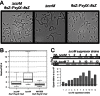
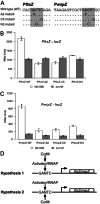
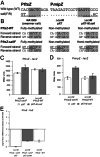
DNA methylation regulates many processes, including gene expression, by superimposing secondary information on DNA sequences. The conserved CcrM enzyme, which methylates adenines in GANTC sequences, is essential to the viability of several Alphaproteobacteria. In this study, we find that Caulobacter crescentus cells lacking the CcrM enzyme accumulate low levels of the two conserved FtsZ and MipZ proteins, leading to a severe defect in cell division. This defect can be compensated by the expression of the ftsZ gene from an inducible promoter or by spontaneous suppressor mutations that promote FtsZ accumulation. We show that CcrM promotes the transcription of the ftsZ and mipZ genes and that the ftsZ and mipZ promoter regions contain a conserved CGACTC motif that is critical to their activities and to their regulation by CcrM. In addition, our results suggest that the ftsZ promoter has the lowest activity when the CGACTC motif is non-methylated, an intermediate activity when it is hemi-methylated and the highest activity when it is fully methylated. The regulation of ftsZ expression by DNA methylation may explain why CcrM is essential in a subset of Alphaproteobacteria.
© 2013 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genomic Adaptations to the Loss of a Conserved Bacterial DNA Methyltransferase.mBio. 2015 Jul 28;6(4):e00952. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00952-15. mBio. 2015. PMID: 26220966 Free PMC article.
-
The functions of DNA methylation by CcrM in Caulobacter crescentus: a global approach.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Apr;42(6):3720-35. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1352. Epub 2014 Jan 7. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24398711 Free PMC article.
-
The CcrM DNA methyltransferase is widespread in the alpha subdivision of proteobacteria, and its essential functions are conserved in Rhizobium meliloti and Caulobacter crescentus.J Bacteriol. 1997 Sep;179(18):5869-77. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.18.5869-5877.1997. J Bacteriol. 1997. PMID: 9294447 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation in Caulobacter and other Alphaproteobacteria during cell cycle progression.Trends Microbiol. 2014 Sep;22(9):528-35. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2014.05.003. Epub 2014 Jun 2. Trends Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24894626 Review.
-
DNA methyltransferases and epigenetic regulation in bacteria.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2016 Sep;40(5):575-91. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuw023. Epub 2016 Jul 29. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27476077 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of (p)ppGpp on the progression of the cell cycle of Caulobacter crescentus.J Bacteriol. 2014 Jul;196(14):2514-25. doi: 10.1128/JB.01575-14. Epub 2014 May 2. J Bacteriol. 2014. PMID: 24794566 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial resistance and mechanisms of epigenetic regulation.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Jun 14;13:1199646. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1199646. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37389209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Epigenetic Regulation of Alpha-Synuclein Expression in Down Syndrome.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Jan;53(1):155-162. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-8979-z. Epub 2014 Nov 23. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 25416858
-
DNA methylation by CcrM contributes to genome maintenance in the Agrobacterium tumefaciens plant pathogen.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Oct 28;52(19):11519-11535. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae757. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 39228370 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Adaptations to the Loss of a Conserved Bacterial DNA Methyltransferase.mBio. 2015 Jul 28;6(4):e00952. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00952-15. mBio. 2015. PMID: 26220966 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

