Deficiency of terminal ADP-ribose protein glycohydrolase TARG1/C6orf130 in neurodegenerative disease
- PMID: 23481255
- PMCID: PMC3642678
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2013.51
Deficiency of terminal ADP-ribose protein glycohydrolase TARG1/C6orf130 in neurodegenerative disease
Abstract
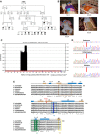
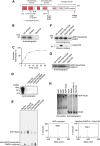
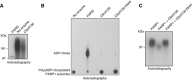
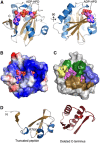
Adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-ribosylation is a post-translational protein modification implicated in the regulation of a range of cellular processes. A family of proteins that catalyse ADP-ribosylation reactions are the poly(ADP-ribose) (PAR) polymerases (PARPs). PARPs covalently attach an ADP-ribose nucleotide to target proteins and some PARP family members can subsequently add additional ADP-ribose units to generate a PAR chain. The hydrolysis of PAR chains is catalysed by PAR glycohydrolase (PARG). PARG is unable to cleave the mono(ADP-ribose) unit directly linked to the protein and although the enzymatic activity that catalyses this reaction has been detected in mammalian cell extracts, the protein(s) responsible remain unknown. Here, we report the homozygous mutation of the c6orf130 gene in patients with severe neurodegeneration, and identify C6orf130 as a PARP-interacting protein that removes mono(ADP-ribosyl)ation on glutamate amino acid residues in PARP-modified proteins. X-ray structures and biochemical analysis of C6orf130 suggest a mechanism of catalytic reversal involving a transient C6orf130 lysyl-(ADP-ribose) intermediate. Furthermore, depletion of C6orf130 protein in cells leads to proliferation and DNA repair defects. Collectively, our data suggest that C6orf130 enzymatic activity has a role in the turnover and recycling of protein ADP-ribosylation, and we have implicated the importance of this protein in supporting normal cellular function in humans.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
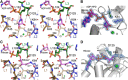
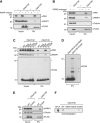


Comment in
-
New players to the field of ADP-ribosylation make the final cut.EMBO J. 2013 May 2;32(9):1205-7. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2013.83. Epub 2013 Apr 9. EMBO J. 2013. PMID: 23572078 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams PD, Afonine PV, Bunkóczi G, Chen VB, Davis IW, Echols N, Headd JJ, Hung LW, Kapral GJ, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, McCoy AJ, Moriarty NW, Oeffner R, Read RJ, Richardson DC, Richardson JS, Terwilliger TC, Zwart PH (2010) PHENIX: a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 66: 213–221 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahel I, Ahel D, Matsusaka T, Clark AJ, Pines J, Boulton SJ, West SC (2008) Poly(ADP-ribose)-binding zinc finger motifs in DNA repair/checkpoint proteins. Nature 451: 81–85 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

