Strain-specific variations in cation content and transport in mouse erythrocytes
- PMID: 23482811
- PMCID: PMC3656420
- DOI: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00143.2012
Strain-specific variations in cation content and transport in mouse erythrocytes
Abstract
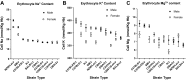
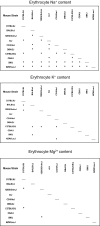
Studies of ion transport pathophysiology in hematological disorders and tests of possible new therapeutic agents for these disorders have been carried out in various mouse models because of close functional similarities between mouse and human red cells. We have explored strain-specific differences in erythrocyte membrane physiology in 10 inbred mouse strains by determining erythrocyte contents of Na(+), K(+), and Mg(2+), and erythrocyte transport of ions via the ouabain-sensitive Na-K pump, the amiloride-sensitive Na-H exchanger (NHE1), the volume and chloride-dependent K-Cl cotransporter (KCC), and the charybdotoxin-sensitive Gardos channel (KCNN4). Our data reveal substantial strain-specific and sex-specific differences in both ion content and trans-membrane ion transport in mouse erythrocytes. These differences demonstrate the feasibility of identifying specific quantitative trait loci for erythroid ion transport and content in genetically standardized inbred mouse strains.
Keywords: KCC; KCNN4; NHE1; Na-K pump; membrane transport.
Figures


References
-
- Armsby CC, Brugnara C, Alper SL. Cation transport in mouse erythrocytes: role of K+-Cl− cotransport in regulatory volume decrease. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 268: C894–C902, 1995 - PubMed
-
- Armsby CC, Stuart-Tilley AK, Alper SL, Brugnara C. Resistance to osmotic lysis in BXD-31 mouse erythrocytes: association with upregulated K-Cl cotransport. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 270: C866–C877, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Benos DJ, Tosteson DC. Cation movements across mouse red blood cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 601: 167–179, 1980 - PubMed
-
- Brugnara C. Use of reticulocyte cellular indices in the diagnosis and treatment of hematological disorders. Int J Clin Lab Res 28: 1–11, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Brugnara C, Armsby CC, De Franceschi L, Crest M, Euclaire MF, Alper SL. Ca2+-activated K+ channels of human and rabbit erythrocytes display distinctive patterns of inhibition by venom peptide toxins. J Memb Biol 147: 71–82, 1995 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

