Biphasic increase of gap junction coupling induced by dipyridamole in the rat aortic A-10 vascular smooth muscle cell line
- PMID: 23483357
- PMCID: PMC3660691
- DOI: 10.1007/s12079-013-0196-4
Biphasic increase of gap junction coupling induced by dipyridamole in the rat aortic A-10 vascular smooth muscle cell line
Abstract
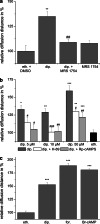
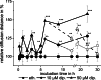
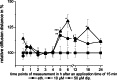
The rat aortic smooth muscle cell line A-10 was used to investigate the effect of dipyridamole on the gap junction coupling of smooth muscle cells. The scrape loading/dye transfer (SL/DT) technique revealed that dipyridamole concentrations between 5 μM and 100 μM significantly increased gap junction coupling. The adenosine receptor antagonist MRS 1754, as well as the PKA inhibitors Rp-cAMPS and H-89 were able to inhibit the dipyridamole-related increase in coupling, while forskolin and Br-cAMP also induced an enhancement of the gap junction coupling. Regarding the time-dependent behaviour of dipyridamole, a short-term effect characterised by an oscillatory reaction was observed for application times of less than 5 h, while applications times of at least 6 h resulted in a long-term effect, characterised by a constant increase of gap junction coupling to its maximum levels. This increase was not altered by prolonged presence of dipyridamole. In parallel, a short application of dipyridamole for at least 15 min was found to be sufficient to evoke the long-term effect measured 6 h after drug washout. We propose that in both the short-term and long-term effect, cAMP-related pathways are activated. The short-term phase could be related to an oscillatory cAMP effect, which might directly affect connexin trafficking, assembly and/or gap junction gating. The long-term effect is most likely related to the new expression and synthesis of connexins. With previous data from a bovine aortic endothelial cell line, the present results show that gap junction coupling of vascular cells is a target for dipyridamole.
Figures

References
-
- Atkinson MM, Lampe PD, Lin HH, Kollander R, Li XR, Kiang DT. Cyclic AMP modifies the cellular distribution of connexin43 and induces a persistent increase in the junctional permeability of mouse mammary tumor cells. J Cell Sci. 1995;108(Pt 9):3079–3090. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin SA, Yao SY, Hyde RJ, Ng AM, Foppolo S, Barnes K, Ritzel MW, Cass CE, Young JD. Functional characterization of novel human and mouse equilibrative nucleoside transporters (hENT3 and mENT3) located in intracellular membranes. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(16):15880–15887. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M414337200. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

