Prognostic factors in myelodysplastic syndromes
- PMID: 23483702
- PMCID: PMC3593279
Prognostic factors in myelodysplastic syndromes
Abstract
Background: Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are clonal disorders of hematopoietic stem cell and are characterized by ineffective hematopoiesis with normo- or hyper cellular bone marrow and cytopenia(s).The natural evolution of the disease consists of bone marrow failure (leading to infectious and hemorrhagic episodes or anemia related complications) and transformation to acute myeloid leukemia. Because MDSs display remarkable clinical, pathologic, and cytogenetic heterogeneity, with variable evolution and survival ranging from months to years, the predictive factors of prognosis have a key role in optimal therapeutic decisions.The purpose of this paper is to analyze prognostic factors within a group of patients diagnosed with myelodysplastic syndromes. The prognostic factors taken into account are: the number and depth of cytopenias, percentage of bone marrow blasts, cytogenetic abnormalities, intensity of anemia and transfusional dependence. These factors are related to overall survival, leukemia free survival, bone marrow failure complications, leukemic evolution, treatment decisions and the response to treatment.
Material and method: The study group comprises of 119 patients diagnosed with de novo MDS, between 2008 and 2011 in the Hematology Department of Coltea Clinical Hospital. In this monitoring period the patients were stratified according to the FAB (French-American-British) morphologic classification.
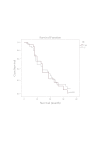
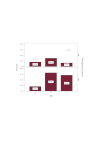
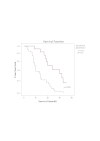
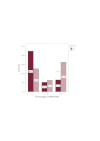
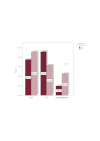
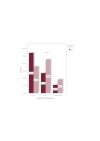
Results: This study revealed that the outcomes of patients with MDS is influenced by the percentage of bone marrow blasts at diagnosis, the number and severity of hematopoietic lineage affected by cytopenia and by the presence of chromosomal abnormalities.
Conclusions: The studied prognostic factors have predictive value in terms of survival, leukemic transformation, treatment response and development of bone marrow failure-related characteristic complications.
Keywords: IPSS; complications; risk groups.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interests regarding this article.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
