Identifying correlations between chromosomal proximity of genes and distance of their products in protein-protein interaction networks of yeast
- PMID: 23483922
- PMCID: PMC3590303
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057707
Identifying correlations between chromosomal proximity of genes and distance of their products in protein-protein interaction networks of yeast
Abstract
In this article we present evidence for a relationship between chromosome gene loci and the topological properties of the protein-protein interaction network corresponding to the set of genes under consideration. Specifically, for each chromosome of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome, the distribution of the intra-chromosome inter-gene distances was analyzed and a positive correlation with the distance among the corresponding proteins of the protein-protein interaction network was found. In order to study this relationship we used concepts based on non-parametric statistics and information theory. We provide statistical evidence that if two genes are closely located, then it is likely that their protein products are closely located in the protein-protein interaction network, or in other words, that they are involved in the same biological process.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


 . In this example the internode distance is equal to one so that
. In this example the internode distance is equal to one so that  is greater than
is greater than  .
.


 .
.
 .
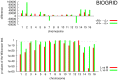
.
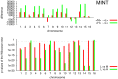
References
-
- Kruglyak S, Tang H (2000) Regulation of adjacent yeast genes. Trends Genet 109–111. - PubMed
-
- Yanai I, Mellor J, DeLisi C (2002) Identifying functional links between genes using conserved chromosomal proximity. Trends Genet 176–179. - PubMed
-
- Batada N, Urrutia A, Hurst L (2006) Chromatin remodelling is a major source of coexpression of linked genes in yeast. Trends Genet 23: 480–484. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

