Valproic acid ameliorates C. elegans dopaminergic neurodegeneration with implications for ERK-MAPK signaling
- PMID: 23485787
- PMCID: PMC3655695
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2013.02.026
Valproic acid ameliorates C. elegans dopaminergic neurodegeneration with implications for ERK-MAPK signaling
Abstract
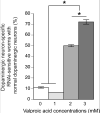
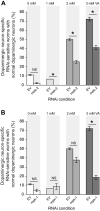
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a currently incurable neurodegenerative disorder that affects the aging population. The loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra is one of the pathological features of PD. The precise causes of PD remain unresolved but evidence supports both environmental and genetic contributions. Current efforts for the treatment of PD are directed toward the discovery of compounds that show promise in impeding age-dependent neurodegeneration in PD patients. Alpha-synuclein (α-Syn) is a human protein that is mutated in specific populations of patients with familial PD. Overexpression of α-Syn in animal models of PD replicates key symptoms of PD, including neurodegeneration. Here, we use the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans as a model system, whereby α-Syn toxicity causes dopaminergic neurodegeneration, to test the capacity of valproic acid (VA) to protect neurons. The results of our study showed that treatment of nematodes with moderate concentrations of VA significantly protects dopaminergic neurons against α-Syn toxicity. Consistent with previously established knowledge related to the mechanistic action of VA in the cell, we showed through genetic analysis that the neuroprotection conferred by VA is inhibited by cell-specific depletion of the C. elegans ortholog of the MAP extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), MPK-1, in the dopaminergic neurons. These findings suggest that VA may exert its neuroprotective effect via ERK-MAPK, or alternately could act with MAPK signaling to additively provide dopaminergic neuroprotection.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Modeling Parkinson's Disease in C. elegans.J Parkinsons Dis. 2018;8(1):17-32. doi: 10.3233/JPD-171258. J Parkinsons Dis. 2018. PMID: 29480229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biofilm proficient Bacillus subtilis prevents neurodegeneration in Caenorhabditis elegans Parkinson's disease models via PMK-1/p38 MAPK and SKN-1/Nrf2 signaling.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 21;15(1):9864. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-93737-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40118903 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic RNA Interference Defective (SID) genes modulate dopaminergic neurodegeneration in C. elegans.PLoS Genet. 2022 Aug 19;18(8):e1010115. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010115. eCollection 2022 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2022. PMID: 35984862 Free PMC article.
-
Carpesii fructus extract exhibits neuroprotective effects in cellular and Caenorhabditis elegans models of Parkinson's disease.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Apr;30(4):e14515. doi: 10.1111/cns.14515. Epub 2023 Oct 31. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 37905594 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Caenorhabditis elegans as Parkinson's Disease Model: Neurotoxins and Genetic Implications.Neurotox Res. 2024 Feb 6;42(1):11. doi: 10.1007/s12640-024-00686-3. Neurotox Res. 2024. PMID: 38319410 Review.
Cited by
-
Probiotic Bacillus subtilis Protects against α-Synuclein Aggregation in C. elegans.Cell Rep. 2020 Jan 14;30(2):367-380.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.12.078. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 31940482 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling Parkinson's Disease in C. elegans.J Parkinsons Dis. 2018;8(1):17-32. doi: 10.3233/JPD-171258. J Parkinsons Dis. 2018. PMID: 29480229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Divalproex sodium modulates nuclear localization of ataxin-3 and prevents cellular toxicity caused by expanded ataxin-3.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2018 May;24(5):404-411. doi: 10.1111/cns.12795. Epub 2018 Jan 9. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2018. PMID: 29318784 Free PMC article.
-
Protein mimetic 2D FAST rescues alpha synuclein aggregation mediated early and post disease Parkinson's phenotypes.Nat Commun. 2024 Apr 30;15(1):3658. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-47980-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38688913 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral Phenotyping and Pathological Indicators of Parkinson's Disease in C. elegans Models.Front Genet. 2017 Jun 13;8:77. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2017.00077. eCollection 2017. Front Genet. 2017. PMID: 28659967 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Biermann J, Grieshaber P, Goebel U, Martin G, Thanos S, Giovanni SD, Lagrèze WA. Valproic Acid–Mediated Neuroprotection and Regeneration in Injured Retinal Ganglion Cells. Invest. Ophth. Vis. Sci. 2010;51:526–534. - PubMed
-
- Christian J, Ximenes M, Crisóstomo E, Verde1 L, Graça M, Viana NGSB. Valproic Acid, a Drug with Multiple Molecular Targets Related to Its Potential Neuroprotective Action. Neuroscience and Medicine. 2012;3:107–123.
-
- Church DL, Guan KL, Lambie EJ. Three genes of the MAP kinase cascade, mek-2, mpk-1/sur-1 and let-60 ras, are required for meiotic cell cycle progression in Caenorhabditis elegans. Development. 1995;121:2525–2535. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

