Inhibition of telomerase activity by oleanane triterpenoid CDDO-Me in pancreatic cancer cells is ROS-dependent
- PMID: 23486104
- PMCID: PMC3632053
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules18033250
Inhibition of telomerase activity by oleanane triterpenoid CDDO-Me in pancreatic cancer cells is ROS-dependent
Abstract
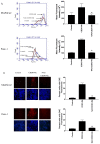
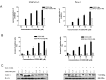
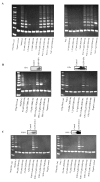
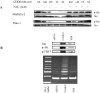
Methyl-2-cyano-3,12-dioxooleana-1,9(11)-dien-28-oate (CDDO-Me) is a synthetic derivative of oleanolic acid, a triterpene, with apoptosis-inducing activity in a wide range of cancer cells. Induction of apoptosis by CDDO-Me is associated with the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inhibition of telomerase activity. In the present study, we investigated the role of ROS in inhibition of telomerase by CDDO-me. Treatment of MiaPaCa-2 and Panc-1 pancreatic cancer cell lines with CDDO-Me induced the production of hydrogen peroxide and superoxide anions and inhibited the telomerase activity. Pretreatment of cells with N-acetylcycsteine, a general purpose antioxidant or overexpression of glutathione peroxidase (GPx) or superoxide dismutase-1 (SOD-1) blocked the telomerase inhibitory activity of CDDO-Me. Furthermore, blocking ROS generation also prevented the inhibition of hTERT gene expression, hTERT protein production and expression of a number of hTERT-regulatory proteins by CDDO-Me (e.g., c-Myc, Sp1, NF-κB and p-Akt). Data also showed that Akt plays an important role in the activation of telomerase activity. Together, these data suggest that inhibition of telomerase activity by CDDO-Me is mediated through a ROS-dependent mechanism; however, more work is needed to fully understand the role of ROS in down-regulation of hTERT gene and hTERT-regulatory proteins by CDDO-Me.
Figures

References
-
- Honda T., Rounds B.V., Bore L., Finlay H.J., Favaloro F.G., Suh N., Wang Y., Sporn M.B., Gribble G.W. Synthetic oleanane and ursane triterpenoids with modified rings A and C: A series of highly active inhibitors of nitric oxide production in mouse macrophages. J. Med. Chem. 2000;43:4233–4246. doi: 10.1021/jm0002230. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ito Y., Pandey P., Sporn M.B., Datta R., Kharbanda S., Kufe D. The novel triterpenoid CDDO induces apoptosis and differentiation of human osteosarcoma cells by a caspase-8 dependent mechanism. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001;59:1094–1099. - PubMed
-
- Konopleva M., Tsao T., Estrov Z., Lee R.M., Wang R.Y., Jackson C.E., McQueen T., Monaco G., Munsell M., Belmont J., et al. The synthetic triterpenoid 2-cyano-3,12-dioxooleana-1,9-dien-28-oic acid induces caspase-dependent and -independent apoptosis in acute myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Res. 2004;64:7927–7935. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-2402. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gao X., Deeb D., Jiang H., Liu Y., Dulchavsky S.A., Gautam S.C. Synthetic triterpenoids inhibit growth and induce apoptosis in human glioblastoma and neuroblastoma cells through inhibition of prosurvival Akt, NF-kappaB and Notch1 signaling. J. Neurooncol. 2007;84:147–157. doi: 10.1007/s11060-007-9364-9. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

