Effectiveness of the power dry-land training programmes in youth swimmers
- PMID: 23486353
- PMCID: PMC3590875
- DOI: 10.2478/v10078-012-0025-5
Effectiveness of the power dry-land training programmes in youth swimmers
Abstract
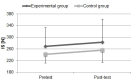
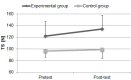
The aim of the study was to evaluate the effects of the dry-land power training on swimming force, swimming performance and strength in youth swimmers. Twenty six male swimmers, free from injuries and training regularly at least 6 times a week, were enrolled in the study and randomly assigned to one of two groups: experimental (n=14, mean age 14.0 ± 0.5 yrs, mean height 1.67±0.08 m and mean body mass 55.71 ±9.55 kg) and control (n=12, mean age 14.1 ± 0.5 yrs, mean height 1.61±0.11 m and mean body mass 49.07 ±8.25 kg). The experimental group took part in a combined swimming and dry-land power training. The control group took part in swimming training only. The training programmes in water included a dominant aerobic work in front crawl. In this research the experimental group tended to present slightly greater improvements in sprint performance. However, the stroke frequency insignificantly decreased (-4.30%, p>0.05) in the experimental group and increased (6.28%, p>0.05) in the control group. The distance per stroke insignificantly increased in the experimental group (5.98%, p>0.05) and insignificantly decreased in the control group (-5.36%, p>0.05). A significant improvement of tethered swimming force for the experimental group (9.64%, p<0.02) was found, whereas the increase was not statistically significant in the control group (2.86%, p>0.05). The main data cannot clearly state that power training allowed an enhancement in swimming performance, although a tendency to improve swimming performance in tethered swimming was noticed.
Keywords: ergometer; strength; tethered force; youth swimmers.
Figures



References
-
- Abernethy P, Quigley B. Concurrent strength and endurance training of the elbow extensors. J Strength Cond Res. 1993;7(7):234–240.
-
- Barbosa TM, Fernandes RJ, Keskinen KL, Vilas-Boas JP. The influence of stroke mechanics into energy cost of elite swimmers. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2008;103(2):139–49. - PubMed
-
- Barbosa TM, Costa MJ, Marinho DA, Coelho J, Moreira M, Silva AJ. Modeling the links between young swimmers’ performance: energetic and biomechanic profiles. Pediatr Exerc Sci. 2010;22(3):379–91. - PubMed
-
- Bigland-Ritchie B. EMG/force relations and fatigue of human voluntary contractions. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 1981;9:75–117. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
