Can Tc 99m DTPA be Used in Adult Patients in Evaluation of Relative Renal Function Measurement as the Reference Tc 99m DMSA Method?
- PMID: 23486843
- PMCID: PMC3590936
- DOI: 10.4274/MIRT.20.03
Can Tc 99m DTPA be Used in Adult Patients in Evaluation of Relative Renal Function Measurement as the Reference Tc 99m DMSA Method?
Abstract
Objective: In the literature, there are many reports comparing relative renal function calculated with Tc 99m DTPA and Tc 99m DMSA in adults and children. However, there is no consensus about the results. As there is indeterminacy in the reliability of Tc 99m DTPA for the calculation of the relative renal functions, we retrospectively designed a study to compare the relative renal functions measured with Tc 99m DMSA and Tc 99m DTPA in adult patients with renal diseases Material and Methods: We retrospectively analyzed the data of 144 patients who applied to Nuclear Medicine Department of three hospitals between 2009 and 2010 and who had both dynamic and static renal imaging. Renal dynamic scintigraphies were compared to the relative function measured using Tc 99m DMSA static scintigraphy. Comparison of relative renal function measurements using dynamic and static renal scintigraphies was performed using Pearson correlation test. The comparison results were expressed with Bland-Altman analysis.
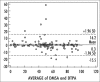
Results: The study was conducted with 144 patients and 288 kidneys. Fifty six of patients were male. Mean age was 39.9±15.2 years. Thirty four patients had hydronephrosis, 28 pyelonephritis, 53 renal calculi, 3 chronic renal failure, 2 acute renal failure, 1 benign renal neoplasia, 15 renal atrophy, 8 ureteropelvic junction stenosis. Relative renal function was calculated in Tc 99m DMSA and 99m Tc-DTPA studies. The mean relative renal functions measured with Tc 99m DTPA was 52.54±23.09% and 47.25±23.09, with Tc 99m DMSA 52.85±21.80% and 47.07±21.77% for right and left kidneys, respectively. In bivariate correlation analysis (Pearson) a significant positive correlation was found between the relative renal functions calculated with Tc 99m DTPA and Tc 99m DMSA (r =0.937, p< 0.001). In Bland-Altman plots, the mean difference between two methods was 0.3 and the correlation limits were between 16.2 to -15.5.
Conclusion: As a result, we concluded that Tc 99m DTPA is also a good method for the relative renal function evaluation when compared to Tc 99m DMSA scan. Although Tc 99m DMSA is the most reliable method for the calculation of relative renal function, Tc 99m DTPA can be another choice for the calculation of relative renal function without a complementary DMSA scan particularly in patients who require renogram curve and GFR calculations.
Conflict of interest: None declared.
Keywords: Relative renal function; Tc 99m DMSA; Tc 99m DTPA; adults.
Figures
References
-
- Moran JK. Technetium-99m-EC and other potential new agents in renal nuclear medicine. Semin Nucl Med. 1999;29:91–101. - PubMed
-
- Taylor A Jr, Lallone R. Differential renal function in unilateral renal injury: possible effects of radiopharmaceutical choice. J Nucl Med. 1985;26:77–80. - PubMed
-
- Ardela Diaz E, Miguel Martinez B, Gutierrez Duenas JM, Diez Pascual R, Garcia Arcal D, Dominguez Vallejo FJ. Comparative study of differential renal function by DMSA and MAG-3 in congenital unilateral uropathies. Cir Pediatr. 2002;15:118–121. - PubMed
-
- Kawashima A, Sandler CM, Goldman SM. Current roles and controversies in the imaging evaluation of acute renal infection. World J Urol. 1998;16:9–17. - PubMed
-
- Piepsz A. Cortical scintigraphy and urinary tract infection in children. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2002;17:560–562. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials