The Agreement Between Blood Pool - Delayed Bone Scintigraphy and Tc-99m Human Immunoglobulin G (HIG) Scintigraphy in the Determination of the Presence and Severity of Inflammatory Arthritis
- PMID: 23487410
- PMCID: PMC3590942
- DOI: 10.4274/MIRT.24
The Agreement Between Blood Pool - Delayed Bone Scintigraphy and Tc-99m Human Immunoglobulin G (HIG) Scintigraphy in the Determination of the Presence and Severity of Inflammatory Arthritis
Abstract
Objective: In this study, it was aimed to investigate the agreement between early phase of bone scintigraphy - human immunoglobulin scintigraphy (EPBS-HIG) and late phase bone scintigraphy - HIG (LPBS-HIG) in the determination of the presence and also the severity of inflammatory arthritis.
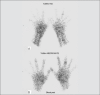
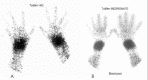
Material and methods: Twenty-eight patients (23 female, 5 male; between 19 to 80 years of age) with inflammatory arthritis were included in the study. Tc-99m HIG and blood pool/late phase bone scintigraphies were performed in all patients. In scintigraphic examinations, the joints were scored with the degree of accumulation of the radiopharmaceutical by the semiquantitative analysis (0=Background activity, 1=Faint uptake, 2=Moderate uptake, 3=Marked uptake) which is called as visually active joint score as severity index of the disease. To estimate the agreement between EPBS - HIG and LPBS - HIG in the determination of the presence and severity of inflammatory arthritis, 2x2 kappa coefficients were calculated.
Results: Our results showed good agreement between EPBS - HIG for the presence of inflammation (kappa: 0.72) but not for the severity of the disease (kappa: 0.29), poor agreement between LPBS - HIG for both the presence (kappa: 0.51) and severity (kappa: 0.01) of inflammatory arthritis.
Conclusion: The blood pool scintigraphy could be used in the investigation of the presence of inflammatory arthritis because the good agreement with HIG and the lower cost but not for the severity of the disease Conflict of interest:None declared.
Keywords: Reactive Arthritis; Rheumatoid Arthritis; Technetium 99m HIG.
Figures

References
-
- Bois MHW, Pauwels EKJ. Arthritis: current status of scintigraphy and future trends. In: Murray IPJ, Ell PJ, editors. Nuclear Medicine in Clinical Diagnosis and Treatment. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 1994. pp. 1041–1054.
-
- Berna L, Torres G, Diez C, Estorch M, Martinez-Duncher D, Carrio I. Technetium-99m human polyclonal immunoglobulin G studies and conventional bone scans to detect active joint inflammation in chronic rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Nucl Med. 1992;19:173–176. - PubMed
-
- Pons F, Moya F, Hernanz R, Sola M, Del Olmo JA, Piera C, Munoz-Gomez J, Setoain J. Detection and quantitative analysis of joint activity inflammation with 99mTc-polyclonal human immunoglobulin G. Nucl Med Commun. 1993;14:225–231. - PubMed
-
- Tishler M, Lysyy O, Levy O, Volkov O, Golan H. 99m Tc-albumin nanocolloid joint scintigraphy in rheumatoid arthritis patients who are in clinical remission-is remission real? Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2010;28(3):360–364. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
