Conversion of peripheral blood NK cells to a decidual NK-like phenotype by a cocktail of defined factors
- PMID: 23487420
- PMCID: PMC3742368
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202582
Conversion of peripheral blood NK cells to a decidual NK-like phenotype by a cocktail of defined factors
Abstract
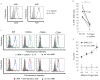
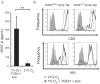
NK cells that populate the decidua are important regulators of normal placentation. In contrast to peripheral blood NK cells, decidual NK (dNK) cells lack cytotoxicity, secrete proangiogenic factors, and regulate trophoblast invasion. In this study we show that exposure to a combination of hypoxia, TGF-β1, and a demethylating agent results in NK cells that express killer cell Ig-like receptors, the dNK cell markers CD9 and CD49a, and a dNK pattern of chemokine receptors. These cells secrete vascular endothelial growth factor (a potent proangiogenic molecule), display reduced cytotoxicity, and promote invasion of human trophoblast cell lines. These findings have potential therapeutic applications for placental disorders associated with altered NK cell biology.
Figures
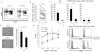
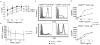


References
-
- Orange JS, Fassett MS, Koopman LA, Boyson JE, Strominger JL. Viral evasion of natural killer cells. Nat Immunol. 2002;3:1006–1012. - PubMed
-
- Vivier E, Tomasello E, Baratin M, Walzer T, Ugolini S. Functions of natural killer cells. Nat Immunol. 2008;9:503–510. - PubMed
-
- Bulmer JN, Morrison L, Longfellow M, Ritson A, Pace D. Granulated lymphocytes in human endometrium: histochemical and immunohistochemical studies. Hum Reprod. 1991;6:791–798. - PubMed
-
- Bulmer JN, Williams PJ, Lash GE. Immune cells in the placental bed. Int J Dev Biol. 2010;54:281–294. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

