Coordinated Mechanosensitivity of Membrane Rafts and Focal Adhesions
- PMID: 23487555
- PMCID: PMC3593241
- DOI: 10.1007/s12195-012-0225-z
Coordinated Mechanosensitivity of Membrane Rafts and Focal Adhesions
Abstract
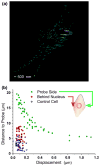
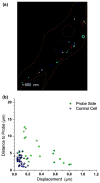
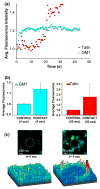
Endothelial cells sense mechanical forces of blood flow through mechanisms that involve focal adhesions (FAs). The mechanosensitive pathways that originate from FA-associated integrin activation may involve membrane rafts, small cholesterol- and sphigolipid-rich domains that are either immobilized, by virtue of their attachment to the cytoskeleton, or highly mobile in the plane of the plasma membrane. In this study, we fluorescently labeled non-mobile and mobile populations of GM1, a ganglioside associated with lipid rafts, and transfected cells with the red fluorescent protein-(RFP-) talin, an indicator of integrin activation at FAs, in order to determine the kinetics and sequential order of raft and talin mechanosensitivity. Cells were imaged under confocal microscopy during mechanical manipulation of a FA induced by a fibronectin (FN)-functionalized nanoelectrode with feedback control of position. First, FA deformation led to long range deformation of immobile rafts followed by active recoil of a subpopulation of displaced rafts. Second, initial adhesion between the FN-probe and the cell induced rapid accumulation of GM1 at the probe site with a time constant of 1.7 s. Talin accumulated approximately 20 s later with a time constant of 0.6 s. Third, a 1 μm deformation of the FA lead to immediate (0.3 s) increase in GM1 fluorescence and a later (6 s) increase in talin. Fourth, long term deformation of FAs led to continual GM1 accumulation at the probe site that was reversed upon removal of the deformation. These results demonstrate that rafts are directly mechanosensitive and that raft mobility may enable the earliest events related to FA mechanosensing and reinforcement upon force application.
Keywords: Endothelial cells; Focal adhesion; Mechanotransduction; Membrane rafts; Scanning ion conductance microscopy; Talin.
Figures






References
-
- Bouaouina M, Lad Y, Calderwood DA. The N-terminal domains of talin cooperate with the phosphotyrosine binding-like domain to activate beta1 and beta3 integrins. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:6118–6125. - PubMed
-
- Brown DA, London E. Structure and function of sphingolipid- and cholesterol-rich membrane rafts. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:17221–17224. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

