Electroencephalogram signatures of loss and recovery of consciousness from propofol
- PMID: 23487781
- PMCID: PMC3607036
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1221180110
Electroencephalogram signatures of loss and recovery of consciousness from propofol
Abstract
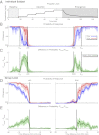
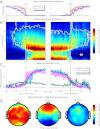
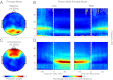
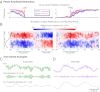
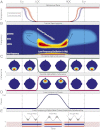
Unconsciousness is a fundamental component of general anesthesia (GA), but anesthesiologists have no reliable ways to be certain that a patient is unconscious. To develop EEG signatures that track loss and recovery of consciousness under GA, we recorded high-density EEGs in humans during gradual induction of and emergence from unconsciousness with propofol. The subjects executed an auditory task at 4-s intervals consisting of interleaved verbal and click stimuli to identify loss and recovery of consciousness. During induction, subjects lost responsiveness to the less salient clicks before losing responsiveness to the more salient verbal stimuli; during emergence they recovered responsiveness to the verbal stimuli before recovering responsiveness to the clicks. The median frequency and bandwidth of the frontal EEG power tracked the probability of response to the verbal stimuli during the transitions in consciousness. Loss of consciousness was marked simultaneously by an increase in low-frequency EEG power (<1 Hz), the loss of spatially coherent occipital alpha oscillations (8-12 Hz), and the appearance of spatially coherent frontal alpha oscillations. These dynamics reversed with recovery of consciousness. The low-frequency phase modulated alpha amplitude in two distinct patterns. During profound unconsciousness, alpha amplitudes were maximal at low-frequency peaks, whereas during the transition into and out of unconsciousness, alpha amplitudes were maximal at low-frequency nadirs. This latter phase-amplitude relationship predicted recovery of consciousness. Our results provide insights into the mechanisms of propofol-induced unconsciousness, establish EEG signatures of this brain state that track transitions in consciousness precisely, and suggest strategies for monitoring the brain activity of patients receiving GA.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: P.L.P. and E.N.B. have a patent pending on anesthesia monitoring.
Figures

References
-
- Palanca BJ, Mashour GA, Avidan MS. Processed electroencephalogram in depth of anesthesia monitoring. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2009;22(5):553–559. - PubMed
-
- Avidan MS, et al. BAG-RECALL Research Group Prevention of intraoperative awareness in a high-risk surgical population. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(7):591–600. - PubMed
-
- Niedermeyer E, Lopes da Silva FH. Electroencephalography: Basic Principles, Clinical Applications, and Related Fields. 5th Ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2005. p. p xiii. 1309.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

