Biomarkers in nutrition: new frontiers in research and application
- PMID: 23488557
- PMCID: PMC3627310
- DOI: 10.1111/nyas.12069
Biomarkers in nutrition: new frontiers in research and application
Abstract
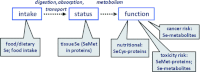
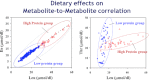
Nutritional biomarkers--biochemical, functional, or clinical indices of nutrient intake, status, or functional effects--are needed to support evidence-based clinical guidance and effective health programs and policies related to food, nutrition, and health. Such indices can reveal information about biological or physiological responses to dietary behavior or pathogenic processes, and can be used to monitor responses to therapeutic interventions and to provide information on interindividual differences in response to diet and nutrition. Many nutritional biomarkers are available; yet there has been no formal mechanism to establish consensus regarding the optimal biomarkers for particular nutrients and applications.
© 2013 New York Academy of Sciences.
Figures




References
-
- Black RE, Allen LH, Bhutta ZA, et al. Maternal and child undernutrition: global and regional exposures and health consequences. Lancet. 2008;371:243–260. - PubMed
-
- Ramakrishnan U. Prevalence of micronutrient malnutrition worldwide. Nutr. Rev. 2002;60:S46–S52. - PubMed
-
- Garcia OP, Long KZ, Rosado JL. Impact of micronutrient deficiencies on obesity. Nutr. Rev. 2009;67:559–672. - PubMed
-
- Global Strategy on Diet, Physical Activity and Health. Geneva: World Health Organization; http://www.who.int/dietphysicalactivity/strategy/eb11344/strategy_englis....
-
- Jehn M, Brewis A. Paradoxical malnutrition in mother-child pairs: untangling the phenomenon of over- and under-nutrition in underdeveloped economies. Econ. Hum. Biol. 2009;7:28–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

