Expression of histamine receptor genes Hrh3 and Hrh4 in rat brain endothelial cells
- PMID: 23488566
- PMCID: PMC3764849
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.12173
Expression of histamine receptor genes Hrh3 and Hrh4 in rat brain endothelial cells
Abstract
Background and purpose: Brain vascular endothelial cells express histamine H1 and H2 receptors, which regulate brain capillary permeability. We investigated whether H3 and H4 receptors are also expressed in these cells and may thus play a role in permeability regulation.
Experimental approach: An immortalized rat brain endothelial cell line RBE4 was used to assess the presence of H3 and H4 receptors. Reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) and sequencing were used to identify the receptor mRNAs. The receptors were stimulated with histamine and immepip, and specific inverse agonists/antagonists ciproxifan and JNJ 7777120 were used to block H3 and H4 receptors, respectively.
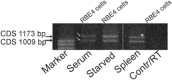
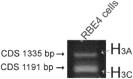
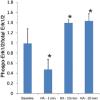
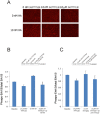
Key results: RT-PCR of mRNA extracted from cultured immortalized RBE4 cells revealed two rat H4 receptor gene (Hrh4) transcripts, one full-length (coding sequence 1173 bp), and one with a 164 bp deletion. Also, two rat H3 receptor gene (Hrh3) isoform mRNAs were expressed in RBE4 cells, and sequencing showed they were the full-length H3 receptor and the 144 bp deletion form. Both histamine and immepip (H3 and H4 receptor agonists) activated the Erk1/2 MAPK pathway in the RBE4 cells and in vivo in brain blood vessels by activating H4 receptors, as the H4 receptor-specific inverse agonists/antagonist JNJ 7777120, but not ciproxifan, H3 receptor antagonist, dose-dependently blocked this effect in RBE4 cells.
Conclusions and implications: Both Hrh3 and Hrh4 receptors are expressed in rat brain endothelial cells, and activation of the histamine H4 receptor activates the Erk1/2 cascade. H3 and H4 receptors in endothelial cells are potentially important for regulation of blood-brain barrier permeability, including trafficking of immunocompetent cells.
Keywords: Erk1/Erk2; GPCR; MAPK; blood-brain barrier; histamine.
© 2013 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2013 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures


References
-
- Akdis CA, Simons FE. Histamine receptors are hot in immunopharmacology. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006;533:69–76. - PubMed
-
- Drutel G, Peitsaro N, Karlstedt K, Wieland K, Smit MJ, Timmerman H, et al. Identification of rat H3 receptor isoforms with different brain expression and signaling properties. Mol Pharmacol. 2001;59:1–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

