HDL and endothelial protection
- PMID: 23488589
- PMCID: PMC3682699
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.12174
HDL and endothelial protection
Abstract
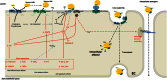
High-density lipoproteins (HDLs) represent a family of particles characterized by the presence of apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I) and by their ability to transport cholesterol from peripheral tissues back to the liver. In addition to this function, HDLs display pleiotropic effects including antioxidant, anti-apoptotic, anti-inflammatory, anti-thrombotic or anti-proteolytic properties that account for their protective action on endothelial cells. Vasodilatation via production of nitric oxide is also a hallmark of HDL action on endothelial cells. Endothelial cells express receptors for apoA-I and HDLs that mediate intracellular signalling and potentially participate in the internalization of these particles. In this review, we will detail the different effects of HDLs on the endothelium in normal and pathological conditions with a particular focus on the potential use of HDL therapy to restore endothelial function and integrity.
© 2013 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2013 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Acton SL, Scherer PE, Lodish HF, Krieger M. Expression cloning of SR-BI, a CD36-related class B scavenger receptor. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:21003–21009. - PubMed
-
- Aird WC. Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: I. Structure, function, and mechanisms. Circ Res. 2007a;100:158–173. - PubMed
-
- Aird WC. Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: II. Representative vascular beds. Circ Res. 2007b;100:174–190. - PubMed
-
- Alwaili K, Bailey D, Awan Z, Bailey SD, Ruel I, Hafiane A, et al. The HDL proteome in acute coronary syndromes shifts to an inflammatory profile. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1821:405–415. - PubMed
-
- Anderson RG. The caveolae membrane system. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:199–225. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

