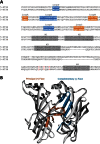
Discriminating between 5-HT₃A and 5-HT₃AB receptors
- PMID: 23489111
- PMCID: PMC3687655
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.12166
Discriminating between 5-HT₃A and 5-HT₃AB receptors
Abstract
The 5-HT3B subunit was first cloned in 1999, and co-expression with the 5-HT3A subunit results in heteromeric 5-HT₃AB receptors that are functionally distinct from homomeric 5-HT₃A receptors. The affinities of competitive ligands at the two receptor subtypes are usually similar, but those of non-competitive antagonists that bind in the pore often differ. A competitive ligand and allosteric modulator that distinguishes 5-HT₃A from 5-HT₃AB receptors has recently been described, and the number of non-competitive antagonists identified with this ability has increased in recent years. In this review, we discuss the differences between 5-HT₃A and 5-HT₃AB receptors and describe the possible sites of action of compounds that can distinguish between them.
© 2013 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2013 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

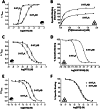
 ) and radioligand binding (
) and radioligand binding ( ) measurements at human 5-HT3A and 5-HT3AB receptors. (A) Concentration–response curves differ at human 5-HT3A and 5-HT3AB receptors. Higher concentrations of 5-HT are needed to elicit a current response at 5-HT3AB receptors and the slope of the curves differs. Parameters derived from these curves are: 5-HT3A, pEC50 = 5.76 ± 0.03, EC50 = 1.74 μM, nH = 2.3, n = 6 and 5-HT3AB, pEC50 = 4.53 ± 0.04, EC50 = 29.5 μM, nH = 1.0, n = 6. (B) Saturation binding with the radioligand [3H]granisetron shows that like many other competitive ligands it has the same affinity at 5-HT3A and 5-HT3AB receptors. Kd values for these representative curves were 0.21 and 0.19 nM for 5-HT3A and 5-HT3AB receptors respectively. (C) Like many other non-competitive antagonists, the sensitivity of 5-HT3R currents to PTX differs at the two receptor types. Parameters derived from these curves are: 5-HT3A, pIC50 = 5.02 ± 0.09, IC50 = 9.55 μM, nH = 0.7, n = 9 and 5-HT3AB, pIC50 = 4.26 ± 0.06, IC50 = 55.0 μM, nH = 0.7, n = 5. (D) VUF10166 is unusual as this competitive antagonist has differing affinities at 5-HT3A and 5-HT3AB receptors. Kd values for these representative curves were 0.08 and 12.6 nM for 5-HT3A and 5-HT3AB receptors respectively. (E) Similar to many other NCAs, the sensitivity of 5-HT3R currents to DTZ also differs at 5-HT3A and 5-HT3AB receptors. Mutagenesis has shown that DTZ has a pore-binding site in the 5-HT3A receptor that is responsible for its increased potency relative to 5-HT3AB receptors. Parameters derived from these curves are: 5-HT3A, pIC50 = 4.68 ± 0.07, IC50 = 20.9 μM, nH = 0.8, n = 7 and 5-HT3AB, pIC50 = 3.53 ± 0.01, IC50 = 295 μM, nH = 0.8, n = 5. (F) In contrast to the electrophysiological measurements shown in panel (E), radioligand competition binding studies show that the binding affinity of DTZ is the same at 5-HT3A and 5-HT3AB receptors. This is consistent with the majority of other competitive antagonists that also have similar binding affinities at the two receptor types. Ki values for these representative curves were 180 μM for 5-HT3A receptors and 169 μM for 5-HT3AB receptors.
) measurements at human 5-HT3A and 5-HT3AB receptors. (A) Concentration–response curves differ at human 5-HT3A and 5-HT3AB receptors. Higher concentrations of 5-HT are needed to elicit a current response at 5-HT3AB receptors and the slope of the curves differs. Parameters derived from these curves are: 5-HT3A, pEC50 = 5.76 ± 0.03, EC50 = 1.74 μM, nH = 2.3, n = 6 and 5-HT3AB, pEC50 = 4.53 ± 0.04, EC50 = 29.5 μM, nH = 1.0, n = 6. (B) Saturation binding with the radioligand [3H]granisetron shows that like many other competitive ligands it has the same affinity at 5-HT3A and 5-HT3AB receptors. Kd values for these representative curves were 0.21 and 0.19 nM for 5-HT3A and 5-HT3AB receptors respectively. (C) Like many other non-competitive antagonists, the sensitivity of 5-HT3R currents to PTX differs at the two receptor types. Parameters derived from these curves are: 5-HT3A, pIC50 = 5.02 ± 0.09, IC50 = 9.55 μM, nH = 0.7, n = 9 and 5-HT3AB, pIC50 = 4.26 ± 0.06, IC50 = 55.0 μM, nH = 0.7, n = 5. (D) VUF10166 is unusual as this competitive antagonist has differing affinities at 5-HT3A and 5-HT3AB receptors. Kd values for these representative curves were 0.08 and 12.6 nM for 5-HT3A and 5-HT3AB receptors respectively. (E) Similar to many other NCAs, the sensitivity of 5-HT3R currents to DTZ also differs at 5-HT3A and 5-HT3AB receptors. Mutagenesis has shown that DTZ has a pore-binding site in the 5-HT3A receptor that is responsible for its increased potency relative to 5-HT3AB receptors. Parameters derived from these curves are: 5-HT3A, pIC50 = 4.68 ± 0.07, IC50 = 20.9 μM, nH = 0.8, n = 7 and 5-HT3AB, pIC50 = 3.53 ± 0.01, IC50 = 295 μM, nH = 0.8, n = 5. (F) In contrast to the electrophysiological measurements shown in panel (E), radioligand competition binding studies show that the binding affinity of DTZ is the same at 5-HT3A and 5-HT3AB receptors. This is consistent with the majority of other competitive antagonists that also have similar binding affinities at the two receptor types. Ki values for these representative curves were 180 μM for 5-HT3A receptors and 169 μM for 5-HT3AB receptors.Similar articles
-
5-Chloroindole: a potent allosteric modulator of the 5-HT₃ receptor.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Jul;169(6):1228-38. doi: 10.1111/bph.12213. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23594147 Free PMC article.
-
Recent developments in 5-HT3 receptor pharmacology.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2013 Feb;34(2):100-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2012.12.002. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23380247 Review.
-
Discovery of a novel allosteric modulator of 5-HT3 receptors: inhibition and potentiation of Cys-loop receptor signaling through a conserved transmembrane intersubunit site.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jul 20;287(30):25241-54. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.360370. Epub 2012 May 15. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22589534 Free PMC article.
-
Agonists and antagonists bind to an A-A interface in the heteromeric 5-HT3AB receptor.Biophys J. 2010 Apr 21;98(8):1494-502. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2009.12.4313. Biophys J. 2010. PMID: 20409468 Free PMC article.
-
5-HT(3) receptors.J Biol Chem. 2012 Nov 23;287(48):40239-45. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R112.406496. Epub 2012 Oct 4. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23038271 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bupropion Inhibits Serotonin Type 3AB Heteromeric Channels at Clinically Relevant Concentrations.Mol Pharmacol. 2020 Mar;97(3):171-179. doi: 10.1124/mol.119.118349. Epub 2019 Dec 23. Mol Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31871303 Free PMC article.
-
5-HT3 Receptor Brain-Type B-Subunits are Differentially Expressed in Heterologous Systems.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015 Jul 15;6(7):1158-64. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.5b00080. Epub 2015 May 7. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25951416 Free PMC article.
-
The antidepressant bupropion is a negative allosteric modulator of serotonin type 3A receptors.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Feb;113(Pt A):89-99. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.09.021. Epub 2016 Sep 24. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 27671323 Free PMC article.
-
The 5-HT3AB receptor shows an A3B2 stoichiometry at the plasma membrane.Biophys J. 2013 Aug 20;105(4):887-98. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2013.07.015. Biophys J. 2013. PMID: 23972841 Free PMC article.
-
International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. CX. Classification of Receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine; Pharmacology and Function.Pharmacol Rev. 2021 Jan;73(1):310-520. doi: 10.1124/pr.118.015552. Pharmacol Rev. 2021. PMID: 33370241 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boess FG, Beroukhim R, Martin IL. Ultrastructure of the 5-hydroxytryptamine3 receptor. J Neurochem. 1995;64:1401–1405. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

