A new de novo missense mutation in MYH2 expands clinical and genetic findings in hereditary myosin myopathies
- PMID: 23489661
- PMCID: PMC3639366
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nmd.2013.02.011
A new de novo missense mutation in MYH2 expands clinical and genetic findings in hereditary myosin myopathies
Abstract
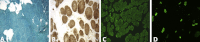
Congenital myopathy related to mutations in myosin MyHC IIa gene (MYH2) is a rare neuromuscular disease. A single dominant missense mutation has been reported so far in a family in which the affected members had congenital joint contractures at birth, external ophthalmoplegia and proximal muscle weakness. Afterward only additional 4 recessive mutations have been identified in 5 patients presenting a mild non-progressive early-onset myopathy associated with ophthalmoparesis. We report a new de novo MYH2 missense mutation in a baby affected by a congenital myopathy characterized by severe dysphagia, respiratory distress at birth and external ophthalmoplegia. We describe clinical, histopathological and muscle imaging findings expanding the clinical and genetic spectrum of MYH2-related myopathy.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Homozygous recessive MYH2 mutation mimicking dominant MYH2 associated myopathy.Neuromuscul Disord. 2018 Aug;28(8):675-679. doi: 10.1016/j.nmd.2018.05.006. Epub 2018 May 21. Neuromuscul Disord. 2018. PMID: 29934118 Free PMC article.
-
Recessive myosin myopathy with external ophthalmoplegia associated with MYH2 mutations.Eur J Hum Genet. 2014 Jun;22(6):801-8. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2013.250. Epub 2013 Nov 6. Eur J Hum Genet. 2014. PMID: 24193343 Free PMC article.
-
Adult onset distal and proximal myopathy with complete ophthalmoplegia associated with a novel de novo p.(Leu1877Pro) mutation in MYH2.Clin Genet. 2015 Dec;88(6):573-8. doi: 10.1111/cge.12552. Epub 2015 Jan 20. Clin Genet. 2015. PMID: 25529940
-
Hereditary myosin myopathies.Neuromuscul Disord. 2007 May;17(5):355-67. doi: 10.1016/j.nmd.2007.02.008. Epub 2007 Apr 16. Neuromuscul Disord. 2007. PMID: 17434305 Review.
-
Thick filament diseases.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;642:78-91. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-84847-1_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 19181095 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical remission of myopathy with MYH2 deficiency after precision medicine-developed rehabilitation: a case report.Am J Transl Res. 2018 Nov 15;10(11):3827-3832. eCollection 2018. Am J Transl Res. 2018. PMID: 30662633 Free PMC article.
-
An E321G MYH1 mutation is strongly associated with nonexertional rhabdomyolysis in Quarter Horses.J Vet Intern Med. 2018 Sep;32(5):1718-1725. doi: 10.1111/jvim.15299. Epub 2018 Aug 5. J Vet Intern Med. 2018. PMID: 30079499 Free PMC article.
-
A novel MYH2 mutation in family members presenting with congenital myopathy, ophthalmoplegia and facial weakness.J Neurol. 2016 Jul;263(7):1427-33. doi: 10.1007/s00415-016-8154-8. Epub 2016 May 13. J Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27177998
-
Homozygous recessive MYH2 mutation mimicking dominant MYH2 associated myopathy.Neuromuscul Disord. 2018 Aug;28(8):675-679. doi: 10.1016/j.nmd.2018.05.006. Epub 2018 May 21. Neuromuscul Disord. 2018. PMID: 29934118 Free PMC article.
-
Dominantly inherited muscle disorders: understanding their complexity and exploring therapeutic approaches.Dis Model Mech. 2024 Oct 1;17(10):dmm050720. doi: 10.1242/dmm.050720. Epub 2024 Nov 6. Dis Model Mech. 2024. PMID: 39501809 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Oldfors A. Hereditary myosin myopathies. Neuromuscul Disord. 2007;17(5):355–367. 2007 Apr 16. Review. - PubMed
-
- Smerdu V., Karsch-Mizrachi I., Campione M., Leinwand L., Schiaffino S. Type IIx myosin heavy chain transcripts are expressed in type IIb fibers of human skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1994;267:1723–1728. - PubMed
-
- Darin N., Kyllerman M., Wahlström J., Martinsson T., Oldfors A. Autosomal dominant myopathy with congenital joint contractures, ophthalmoplegia, and rimmed vacuoles. Ann Neurol. 1998;44(2):242–248. - PubMed
-
- Tajsharghi H., Darin N., Rekabdar E. Mutations and sequence variation in the human myosin heavy chain IIa gene (MYH2) Eur J Hum Genet. 2005;13(5):617–622. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

