Cost of post-weaning multi-systemic wasting syndrome and porcine circovirus type-2 subclinical infection in England - an economic disease model
- PMID: 23490147
- PMCID: PMC3652492
- DOI: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2013.02.010
Cost of post-weaning multi-systemic wasting syndrome and porcine circovirus type-2 subclinical infection in England - an economic disease model
Abstract
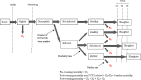
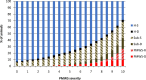
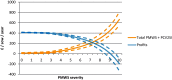
Post-weaning multi-systemic wasting syndrome (PMWS) is a multi-factorial disease with major economic implications for the pig industry worldwide. The present study aimed to assess the economic impact of PMWS and porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2) subclinical infections (PCV2SI) for farrow-to-finish farms and to estimate the resulting cost to the English pig industry. A disease model was built to simulate the varying proportions of pigs in a batch that get infected with PCV2 and develop either PMWS, subclinical disease (reduce growth without evident clinical signs) or remain healthy (normal growth and no clinical signs), depending on the farm level PMWS severity. This PMWS severity measure accounted for the level of post-weaning mortality, PMWS morbidity and proportion of PCV2 infected pigs observed on farms. The model generated six outcomes: infected pigs with PMWS that die (PMWS-D); infected pigs with PMWS that recover (PMWS-R); subclinical pigs that die (Sub-D); subclinical pigs that reach slaughter age (Sub-S); healthy pigs sold (H-S); and pigs, infected or non-infected by PCV2, that die due to non-PCV2 related causes (nonPCV2-D). Enterprise and partial budget analyses were used to assess the deficit/profits and the extra costs/extra benefits of a change in disease status, respectively. Results from the economic analysis at pig level were combined with the disease model's estimates of the proportion of different pigs produced at different severity scores to assess the cost of PMWS and subclinical disease at farm level, and these were then extrapolated to estimate costs at national level. The net profit for a H-S pig was £19.2. The mean loss for a PMWS-D pig was £84.1 (90% CI: 79.6-89.1), £24.5 (90% CI: 15.1-35.4) for a PMWS-R pig, £82.3 (90% CI: 78.1-87.5) for a Sub-D pig, and £8.1 (90% CI: 2.18-15.1) for a Sub-S pig. At farm level, the greatest proportion of negative economic impact was attributed to PCV2 subclinical pigs. The economic impact for the English pig industry for the year 2008, prior to the introduction of PCV2 vaccines, was estimated at £52.6 million per year (90% CI: 34.7-72.0), and approximately £88 million per year during the epidemic period. This was the first study to use empirical data to model the cost of PMWS/PCV2SI at different farm severity levels. Results from this model will be used to assess the efficiency of different control measures and to provide a decision support tool to farmers and policy makers.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Alarcon P., Velasova M., Mastin A., Nevel A., Stark K.D., Wieland B. Farm level risk factors associated with severity of post-weaning multi-systemic wasting syndrome. Prev. Vet. Med. 2011;101:182–191. - PubMed
-
- Alarcon P., Velasova M., Werling D., Stärk K.D.C., Chang Y., Nevel A., Pfeiffer D.U., Wieland B. Assessment and quantification of post-weaning multi-systemic wasting syndrome severity at farm level. Prev. Vet. Med. 2011;98:19–28. - PubMed
-
- Allan G., Meehan B., Todd D., Kennedy S., McNeilly F., Ellis J., Clark E.G., Harding J., Espuna E., Botner A., Charreyre C. Novel porcine circoviruses from pigs with wasting disease syndromes. Vet. Rec. 1998;142:467–468. - PubMed
-
- Anonymous, 2010. Pig Yearbook 2010. BPEX.
-
- Anonymous, 2011. Pig Yearbook 2011. BPEX.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

