miR-200b inhibits TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes growth of intestinal epithelial cells
- PMID: 23492772
- PMCID: PMC3613822
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2013.22
miR-200b inhibits TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes growth of intestinal epithelial cells
Abstract
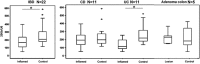
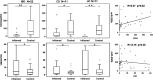
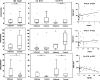
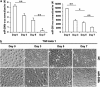
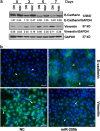
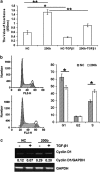
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which consists of Crohn's disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), is a chronic, inflammatory disorder of the gastro-intestinal tract with unknown etiology. Current evidence suggests that intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) is prominently linked to the pathogenesis of IBD. Therefore, maintaining the intact of epithelium has potential roles in improving pathophysiology and clinical outcomes of IBD. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) act as post-transcriptional gene regulators and regulate many biological processes, including embryonal development, cell differentiation, apoptosis and proliferation. In this study, we found that miR-200b decreased significantly in inflamed mucosa of IBD, especially for UC, when compared with their adjacent normal tissue. Simultaneously, we also found that the genes of E-cadherin and cyclin D1 were reduced significantly and correlated positively to the miR-200b. In addition, the upregulation of transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1) was inversely correlated to the miR-200b in IBD. To investigate the possible roles of miR-200b in IECs maintaining, we used TGF-β1 to induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in IEC-6 initially. After sustained over-expressing miR-200b in IEC-6, the EMT was inhibited significantly that was characterized by downregulation of vimentin and upregulation of E-cadherin. Furthermore, we found that miR-200b enhanced E-cadherin expression through targeting of ZEB1, which encode transcriptional repressors of E-cadherin. SMAD2 was found to act as a target of miR-200b with direct evidence that miR-200b binding to the 3' UTR of SAMD2 and the ability of miR-200b to repress SMAD2 protein expression. With SMAD2 depletion, the expression of vimentin decreased correspondingly, which suggested miR-200b might reduce vimentin through regulating the SMAD2. With endogenous over-expression of miR-200b, the proliferation of IEC-6 cells increased significantly by increasing S-phase entry and promoting expression of the protein cyclin D1. Summarily, our study suggested a potential role for mir-200b in maintaining intact of intestinal epithelium through inhibiting EMT and promoting proliferation of IECs.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

