MiR-210 promotes a hypoxic phenotype and increases radioresistance in human lung cancer cell lines
- PMID: 23492775
- PMCID: PMC3615727
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2013.71
MiR-210 promotes a hypoxic phenotype and increases radioresistance in human lung cancer cell lines
Abstract
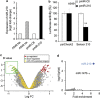
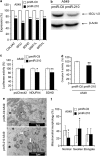
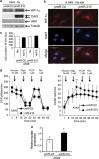
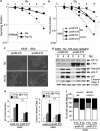
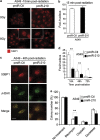
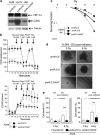
The resistance of hypoxic cells to radiotherapy and chemotherapy is a major problem in the treatment of cancer. Recently, an additional mode of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-dependent transcriptional regulation, involving modulation of a specific set of micro RNAs (miRNAs), including miR-210, has emerged. We have recently shown that HIF-1 induction of miR-210 also stabilizes HIF-1 through a positive regulatory loop. Therefore, we hypothesized that by stabilizing HIF-1 in normoxia, miR-210 may protect cancer cells from radiation. We developed a non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC)-derived cell line (A549) stably expressing miR-210 (pmiR-210) or a control miRNA (pmiR-Ctl). The miR-210-expressing cells showed a significant stabilization of HIF-1 associated with mitochondrial defects and a glycolytic phenotype. Cells were subjected to radiation levels ranging from 0 to 10 Gy in normoxia and hypoxia. Cells expressing miR-210 in normoxia had the same level of radioresistance as control cells in hypoxia. Under hypoxia, pmiR-210 cells showed a low mortality rate owing to a decrease in apoptosis, with an ability to grow even at 10 Gy. This miR-210 phenotype was reproduced in another NSCLC cell line (H1975) and in HeLa cells. We have established that radioresistance was independent of p53 and cell cycle status. In addition, we have shown that genomic double-strand breaks (DSBs) foci disappear faster in pmiR-210 than in pmiR-Ctl cells, suggesting that miR-210 expression promotes a more efficient DSB repair. Finally, HIF-1 invalidation in pmiR-210 cells removed the radioresistant phenotype, showing that this mechanism is dependent on HIF-1. In conclusion, miR-210 appears to be a component of the radioresistance of hypoxic cancer cells. Given the high stability of most miRNAs, this advantage could be used by tumor cells in conditions where reoxygenation has occurred and suggests that strategies targeting miR-210 could enhance tumor radiosensitization.
Figures
Similar articles
-
miR-210 is overexpressed in late stages of lung cancer and mediates mitochondrial alterations associated with modulation of HIF-1 activity.Cell Death Differ. 2011 Mar;18(3):465-78. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2010.119. Epub 2010 Oct 1. Cell Death Differ. 2011. PMID: 20885442 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Damage and Inflammatory Response of p53 Null H358 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells to X-Ray Exposure Under Chronic Hypoxia.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 23;25(23):12590. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312590. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684302 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB in the Radiation Response of A549 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells to X-rays and Carbon Ions under Hypoxia.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 19;25(8):4495. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084495. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38674080 Free PMC article.
-
miR-210: More than a silent player in hypoxia.IUBMB Life. 2011 Feb;63(2):94-100. doi: 10.1002/iub.427. Epub 2011 Feb 24. IUBMB Life. 2011. PMID: 21360638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The dual role of MiR-210 in the aetiology of cancer: A focus on hypoxia-inducible factor signalling.Pathol Res Pract. 2024 Jan;253:155018. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.155018. Epub 2023 Dec 6. Pathol Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 38070222 Review.
Cited by
-
LncRNA PCNAP1 modulates hepatitis B virus replication and enhances tumor growth of liver cancer.Theranostics. 2019 Jul 9;9(18):5227-5245. doi: 10.7150/thno.34273. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 31410212 Free PMC article.
-
Skeletal muscle MiR-210 expression is associated with mitochondrial function in peripheral artery disease patients.Transl Res. 2022 Aug;246:66-77. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2022.03.003. Epub 2022 Mar 12. Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35288364 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue-specific and exosomal miRNAs in lung cancer radiotherapy: from regulatory mechanisms to clinical implications.Cancer Manag Res. 2019 May 13;11:4413-4424. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S198966. eCollection 2019. Cancer Manag Res. 2019. PMID: 31191004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of Mir-144-ZFX pathway in growth regulation of non-small-cell lung cancer.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 16;8(9):e74175. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074175. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24066116 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Epigenetics Regulating Inflammation in Cancer and Aging.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jul 12;10:929708. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.929708. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35903542 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gray LH, Conger AD, Ebert M, Hornsey S, Scott OC. The concentration of oxygen dissolved in tissues at the time of irradiation as a factor in radiotherapy. Br J Radiol. 1953;26:638–648. - PubMed
-
- Palcic B, Skarsgard LD. Reduced oxygen enhancement ratio at low doses of ionizing radiation. Radiat Res. 1984;100:328–339. - PubMed
-
- Harada H. How can we overcome tumor hypoxia in radiation therapy. J Radiat Res. 2011;52:545–556. - PubMed
-
- Ryan HE, Poloni M, McNulty W, Elson D, Gassmann M, Arbeit JM, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha is a positive factor in solid tumor growth. Cancer Res. 2000;60:4010–4015. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

