Synthesis of peptide radiopharmaceuticals for the therapy and diagnosis of tumor diseases
- PMID: 23493103
- PMCID: PMC6269889
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules18033379
Synthesis of peptide radiopharmaceuticals for the therapy and diagnosis of tumor diseases
Abstract
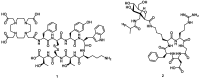
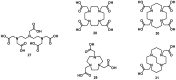
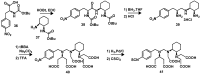
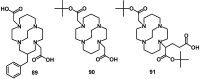
Despite the advances in molecular biology and biochemistry, the prognosis of patients suffering from tumor diseases remains poor. The limited therapeutic success can be explained by the insufficient performance of the common chemotherapeutic drugs that lack the ability to specifically target tumor tissues. Recently peptide radiopharmaceuticals have been developed that enable the concurrent imaging and therapy of tumors expressing a specific target. Here, with a special emphasis on the synthesis of the building blocks required for the complexation of metallic radioisotopes, the requirements to the.
Figures
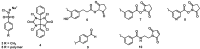
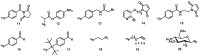
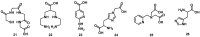
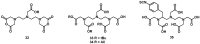


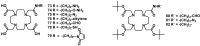
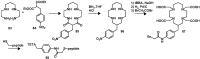
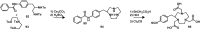
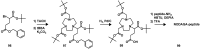
Similar articles
-
Neovascular targeting with cyclic RGD peptide (cRGDf-ACHA) to enhance delivery of radioimmunotherapy.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2000 Feb;15(1):71-9. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2000.15.71. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2000. PMID: 10740655
-
Chelating systems for (99m)Tc/(188)Re in the development of radiolabeled peptide pharmaceuticals.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2012 Jun;12(5):428-61. doi: 10.2174/187152012800617821. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22292757 Review.
-
The synthesis of D-trihydroxyllysine-based oligopeptides as a hydrophilic scaffold and its application to the synthesis of bifunctional chelating agents for use as bone tracers.Chem Asian J. 2008 Dec 1;3(12):2033-45. doi: 10.1002/asia.200800250. Chem Asian J. 2008. PMID: 18956475
-
Radiometallation of receptor-specific peptides for diagnosis and treatment of human cancer.In Vivo. 2005 Jan-Feb;19(1):9-29. In Vivo. 2005. PMID: 15796153 Review.
-
Targeted tumor diagnosis and therapy with peptide hormones as radiopharmaceuticals.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2008 Feb;8(2):186-99. doi: 10.2174/187152008783497046. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18288921 Review.
Cited by
-
Radiolabeled cyclic RGD peptides as radiotracers for tumor imaging.Biophys Rep. 2016;2(1):1-20. doi: 10.1007/s41048-016-0021-8. Epub 2016 Apr 12. Biophys Rep. 2016. PMID: 27819026 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptide Conjugates with Small Molecules Designed to Enhance Efficacy and Safety.Molecules. 2019 May 14;24(10):1855. doi: 10.3390/molecules24101855. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31091786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Affibody-based molecular probe 99mTc-(HE)3ZHER2:V2 for non-invasive HER2 detection in ovarian and breast cancer xenografts.Open Med (Wars). 2024 Sep 3;19(1):20241027. doi: 10.1515/med-2024-1027. eCollection 2024. Open Med (Wars). 2024. PMID: 39247440 Free PMC article.
-
A convenient and efficient total solid-phase synthesis of DOTA-functionalized tumor-targeting peptides for PET imaging of cancer.EJNMMI Res. 2019 Sep 10;9(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s13550-019-0539-0. EJNMMI Res. 2019. PMID: 31502101 Free PMC article.
-
[68Ga]Ga-DFO-c(RGDyK): Synthesis and Evaluation of Its Potential for Tumor Imaging in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 9;22(14):7391. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147391. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34299008 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smith M.R., Li H., Gordon L., Gascoyne R.D., Paietta E., Forero-Torres A., Kahl B.S., Advani R., Hong F., Horning S.J. Phase II study of rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone immunochemotherapy followed by yttrium-90-ibritumomab tiuxetan in untreated mantle-cell lymphoma: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Study E1499. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012;30:3119–3126. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.42.2444. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

