Construction and characterization of novel, completely human serine protease therapeutics targeting Her2/neu
- PMID: 23493312
- PMCID: PMC4410687
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0002
Construction and characterization of novel, completely human serine protease therapeutics targeting Her2/neu
Abstract
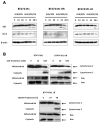
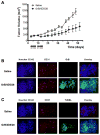
Immunotoxins containing bacterial or plant toxins have shown promise in cancer-targeted therapy, but their long-term clinical use may be hampered by vascular leak syndrome and immunogenicity of the toxin. We incorporated human granzyme B (GrB) as an effector and generated completely human chimeric fusion proteins containing the humanized anti-Her2/neu single-chain antibody 4D5 (designated GrB/4D5). Introduction of a pH-sensitive fusogenic peptide (designated GrB/4D5/26) resulted in comparatively greater specific cytotoxicity although both constructs showed similar affinity to Her2/neu-positive tumor cells. Compared with GrB/4D5, GrB/4D5/26 showed enhanced and long-lasting cellular uptake and improved delivery of GrB to the cytosol of target cells. Treatment with nanomolar concentrations of GrB/4D5/26 resulted in specific cytotoxicity, induction of apoptosis, and efficient downregulation of PI3K/Akt and Ras/ERK pathways. The endogenous presence of the GrB proteinase inhibitor 9 did not impact the response of cells to the fusion construct. Surprisingly, tumor cells resistant to lapatinib or Herceptin, and cells expressing MDR-1 resistant to chemotherapeutic agents showed no cross-resistance to the GrB-based fusion proteins. Administration (intravenous, tail vein) of GrB/4D5/26 to mice bearing BT474 M1 breast tumors resulted in significant tumor suppression. In addition, tumor tissue excised from GrB/4D5/26-treated mice showed excellent delivery of GrB to tumors and a dramatic induction of apoptosis compared with saline treatment. This study clearly showed that the completely human, functionalized GrB construct can effectively target Her2/neu-expressing cells and displays impressive in vitro and in vivo activity. This construct should be evaluated further for clinical use.
©2013 AACR
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- De LC, D’Alessio G. From immunotoxins to immunoRNases. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2008;9:210–4. - PubMed
-
- Frankel AE. Reducing the immune response to immunotoxin. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:13–5. - PubMed
-
- Smallshaw JE, Ghetie V, Rizo J, Fulmer JR, Trahan LL, Ghetie MA, et al. Genetic engineering of an immunotoxin to eliminate pulmonary vascular leak in mice. Nat Biotechnol. 2003;21:387–91. - PubMed
-
- Posey JA, Khazaeli MB, Bookman MA, Nowrouzi A, Grizzle WE, Thornton J, et al. A phase I trial of the single-chain immunotoxin SGN-10 (BR96 sFv-PE40) in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8:3092–9. - PubMed
-
- Hall PD, Virella G, Willoughby T, Atchley DH, Kreitman RJ, Frankel AE. Antibody response to DT-GM, a novel fusion toxin consisting of a truncated diphtheria toxin (DT) linked to human granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM), during a phase I trial of patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Immunol. 2001;100:191–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

