The Massachusetts General Hospital acute stroke imaging algorithm: an experience and evidence based approach
- PMID: 23493340
- PMCID: PMC3623036
- DOI: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2013-010715
The Massachusetts General Hospital acute stroke imaging algorithm: an experience and evidence based approach
Abstract
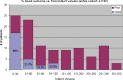
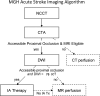
The Massachusetts General Hospital Neuroradiology Division employed an experience and evidence based approach to develop a neuroimaging algorithm to best select patients with severe ischemic strokes caused by anterior circulation occlusions (ACOs) for intravenous tissue plasminogen activator and endovascular treatment. Methods found to be of value included the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS), non-contrast CT, CT angiography (CTA) and diffusion MRI. Perfusion imaging by CT and MRI were found to be unnecessary for safe and effective triage of patients with severe ACOs. An algorithm was adopted that includes: non-contrast CT to identify hemorrhage and large hypodensity followed by CTA to identify the ACO; diffusion MRI to estimate the core infarct; and NIHSS in conjunction with diffusion data to estimate the clinical penumbra.
Figures


References
-
- Baron JC. Mapping the ischaemic penumbra with PET: implications for acute stroke treatment. Cerebrovasc Dis 1999;9:193–201. - PubMed
-
- Jauch EC, Saver JL, Adams HP, Jr, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2013;44:870–947. - PubMed
-
- Yoo AJ, Chaudhry ZA, Nogueira RG, et al. Infarct volume is a pivotal biomarker after intra-arterial stroke therapy. Stroke 2012;43:1323–30. - PubMed
-
- Zaidi SF, Aghaebrahim A, Urra X, et al. Final infarct volume is a stronger predictor of outcome than recanalization in patients with proximal middle cerebral artery occlusion treated with endovascular therapy. Stroke 2012;43:3238–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
