Active muscle regeneration following eccentric contraction-induced injury is similar between healthy young and older adults
- PMID: 23493365
- PMCID: PMC4152159
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01350.2012
Active muscle regeneration following eccentric contraction-induced injury is similar between healthy young and older adults
Abstract
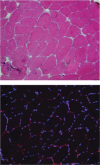
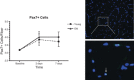
Repair of skeletal muscle after injury is a key aspect of maintaining proper musculoskeletal function. Studies have suggested that regenerative processes, including myogenesis and angiogenesis, are impaired during advanced age, but evidence from humans is limited. This study aimed to compare active muscle regeneration between healthy young and older adults. We evaluated changes in clinical, biochemical, and immunohistochemical indices of muscle regeneration at precisely 2 (T2) and 7 (T3) days following acute muscle injury. Men and women, aged 18-30 and ≥70 years, matched for gender and body mass index, performed 150 unilateral, eccentric contractions of the plantar flexors at 110% of one repetition maximum. Data were analyzed using analysis of covariance, adjusted for gender, habitual physical activity, and baseline level of the outcome. A total of 30 young (n = 15; 22.5 ± 3.7 yr) and older (n = 15; 75.8 ± 5.0 yr) adults completed the study. Following muscle injury, force production declined 16% and 14% in young and older adults, respectively, by T2 and in each group, returned to 93% of baseline strength by T3. Despite modest differences in the pattern of response, postinjury changes in intramuscular concentrations of myogenic growth factors and number of myonuclear (4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole+ and paired box 7+) cells were largely similar between groups. Likewise, postinjury changes in serum and intramuscular indices of inflammation (e.g., TNF-α and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1) and angiogenesis (e.g., VEGF and kinase insert domain receptor) did not differ significantly between groups. These findings suggest that declines in physical activity and increased co-morbidity may contribute to age-related impairments in active muscle regeneration rather than aging per se.
Keywords: aging; angiogenesis; inflammation; myogenesis; skeletal muscle.
Copyright © 2014 the American Physiological Society.
Figures




References
-
- Afilalo J, Eisenberg MJ, Morin JF, Bergman H, Monette J, Noiseux N, Perrault LP, Alexander KP, Langlois Y, Dendukuri N, Chamoun P, Kasparian G, Robichaud S, Gharacholou SM, Boivin JF. Gait speed as an incremental predictor of mortality and major morbidity in elderly patients undergoing cardiac surgery. J Am Coll Cardiol 56: 1668–1676, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Baker BA, Cutlip RG. Skeletal muscle injury versus adaptation with aging: novel insights on perplexing paradigms. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 38: 10–16, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Bamman MM, Ragan RC, Kim JS, Cross JM, Hill VJ, Tuggle SC, Allman RM. Myogenic protein expression before and after resistance loading in 26- and 64-yr-old men and women. J Appl Physiol 97: 1329–1337, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Brack AS, Conboy MJ, Roy S, Lee M, Kuo CJ, Keller C, Rando TA. Increased Wnt signaling during aging alters muscle stem cell fate and increases fibrosis. Science 317: 807–810, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

