Recurrent giant hemangiomas of liver: Report of two rare cases with literature review
- PMID: 23494295
- PMCID: PMC3596508
- DOI: 10.4240/wjgs.v4.i11.262
Recurrent giant hemangiomas of liver: Report of two rare cases with literature review
Abstract
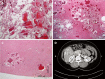
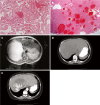
Most hepatic hemangiomas (HHs) are small, asymptomatic and do not require clinical intervention. Surgical resection is only indicated for symptomatic hemangiomas. We report here cases of recurrent HHs in 2 women of 37 and 40 years old, who initially presented with abdominal pain and mass. Radiological examination of each tumor revealed a solitary tumor of 14 and 20 cm in diameter, respectively. Surgical liver segmental resections were performed in both, and the diagnosis of cavernous hemangioma was confirmed. Both patients had recurrent tumor on subsequent radiological examination 4-5 years after the initial surgery. In the first patient, a 15 cm recurrent hemangioma was resected, but multiple hemangiomas were again detected 8 years later occupying the other hepatic lobe, which was not amendable for resection. In the second patient, a 16 cm hemangioma was seen on radiogram, and because the lesion was not symptomatic, conservative observation was offered. Recurrence after liver resection of giant hemangioma is extremely rare. The pathogenesis of tumor progression and recurrence is unknown, as is the management of these patients with recurrent hemangioma, particularly when it is extensive and unresectable.
Keywords: Giant hemangioma; Liver; Recurrent hemangioma.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Giant pedunculated hepatic hemangioma accompanied by a 10-year history of taking oral contraceptive: A case report and literature review.Clin Case Rep. 2024 May 26;12(6):e8995. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.8995. eCollection 2024 Jun. Clin Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38803323 Free PMC article.
-
Combined surgical treatment of giant cavernous hepatic hemangioma: A case report.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2022 May;94:107012. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2022.107012. Epub 2022 Apr 2. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35421729 Free PMC article.
-
Giant cavernous liver hemangiomas: is it the time to change the size categories?Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2016 Feb;15(1):21-9. doi: 10.1016/s1499-3872(15)60035-2. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2016. PMID: 26818540 Review.
-
Surgical Treatment of Giant Liver Hemangioma, Case Report and Literature Review.Sisli Etfal Hastan Tip Bul. 2019 Aug 28;53(3):318-321. doi: 10.14744/SEMB.2017.09815. eCollection 2019. Sisli Etfal Hastan Tip Bul. 2019. PMID: 32377104 Free PMC article.
-
Management of giant liver hemangiomas: an update.Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 Mar;7(3):263-8. doi: 10.1586/egh.13.10. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23445235 Review.
Cited by
-
Systematic Review: Effectiveness of Carbon Dioxide Lasers for Treatment of Adult Laryngeal Hemangioma.J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2025 Jan-Dec;54:19160216251314789. doi: 10.1177/19160216251314789. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2025. PMID: 39865731 Free PMC article.
-
An uncommon cause of a giant abdominal mass.Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2023;16(1):539-541. doi: 10.22037/ghfbb.v16i1.2649. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2023. PMID: 37070115 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bioulac-Sage P, Laumonier H, Laurent C, Blanc JF, Balabaud C. Benign and malignant vascular tumors of the liver in adults. Semin Liver Dis. 2008;28:302–314. - PubMed
-
- Demircan O, Demiryurek H, Yagmur O. Surgical approach to symptomatic giant cavernous hemangioma of the liver. Hepatogastroenterology. 2005;52:183–186. - PubMed
-
- Gourgiotis S, Moustafellos P, Zavos A, Dimopoulos N, Vericouki C, Hadjiyannakis EI. Surgical treatment of hepatic haemangiomas: a 15-year experience. ANZ J Surg. 2006;76:792–795. - PubMed
-
- Schnelldorfer T, Ware AL, Smoot R, Schleck CD, Harmsen WS, Nagorney DM. Management of giant hemangioma of the liver: resection versus observation. J Am Coll Surg. 2010;211:724–730. - PubMed
-
- Bauland CG, van Steensel MA, Steijlen PM, Rieu PN, Spauwen PH. The pathogenesis of hemangiomas: a review. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006;117:29e–35e. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

