A systematic evaluation of miRNA:mRNA interactions involved in the migration and invasion of breast cancer cells
- PMID: 23497265
- PMCID: PMC3599769
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-11-57
A systematic evaluation of miRNA:mRNA interactions involved in the migration and invasion of breast cancer cells
Abstract
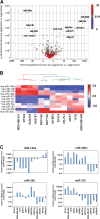
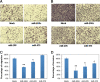
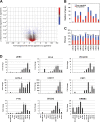
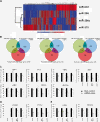
In this study we performed a systematic evaluation of functional miRNA-mRNA interactions associated with the invasiveness of breast cancer cells using a combination of integrated miRNA and mRNA expression profiling, bioinformatics prediction, and functional assays. Analysis of the miRNA expression identified 11 miRNAs that were differentially expressed, including 7 down-regulated (miR-200c, miR-205, miR-203, miR-141, miR-34a, miR-183, and miR-375) and 4 up-regulated miRNAs (miR-146a, miR-138, miR-125b1 and miR-100), in invasive cell lines when compared to normal and less invasive cell lines. Transfection of miR-200c, miR-205, and miR-375 mimics into MDA-MB-231 cells led to the inhibition of in vitro cell migration and invasion. The integrated analysis of miRNA and mRNA expression identified 35 known and novel target genes of miR-200c, miR-205, and mir-375, including CFL2, LAMC1, TIMP2, ZEB1, CDH11, PRKCA, PTPRJ, PTPRM, LDHB, and SEC23A. Surprisingly, the majority of these genes (27 genes) were target genes of miR-200c, suggesting that miR-200c plays a pivotal role in regulating the invasiveness of breast cancer cells. We characterized one of the target genes of miR-200c, CFL2, and demonstrated that CFL2 is overexpressed in aggressive breast cancer cell lines and can be significantly down-regulated by exogenous miR-200c. Tissue microarray analysis further revealed that CFL2 expression in primary breast cancer tissue correlated with tumor grade. The results obtained from this study may improve our understanding of the role of these candidate miRNAs and their target genes in relation to breast cancer invasiveness and ultimately lead to the identification of novel biomarkers associated with prognosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Integrated analysis of mRNA and miRNA profiles revealed the role of miR-193 and miR-210 as potential regulatory biomarkers in different molecular subtypes of breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2021 Jan 18;21(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07731-2. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33461524 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated miRNA and mRNA expression profiling in inflamed colon of patients with ulcerative colitis.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 29;9(12):e116117. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116117. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25546151 Free PMC article.
-
miR-142-3p as tumor suppressor miRNA in the regulation of tumorigenicity, invasion and migration of human breast cancer by targeting Bach-1 expression.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Jun;234(6):9816-9825. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27670. Epub 2018 Nov 27. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30480817
-
[miRNA-16 AS an Internal Control in Breast Cancer Studies: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2021 Nov-Dec;55(6):1045-1056. doi: 10.31857/S0026898421060136. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2021. PMID: 34837708 Russian.
-
Role and Involvement of TENM4 and miR-708 in Breast Cancer Development and Therapy.Cells. 2022 Jan 5;11(1):172. doi: 10.3390/cells11010172. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35011736 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Systems-level Analysis Reveals Multiple Modulators of Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition and Identifies DNAJB4 and CD81 as Novel Metastasis Inducers in Breast Cancer.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2019 Sep;18(9):1756-1771. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA119.001446. Epub 2019 Jun 20. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2019. PMID: 31221721 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA expression as risk biomarker of breast cancer metastasis: a pilot retrospective case-cohort study.BMC Cancer. 2014 Oct 2;14:739. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-739. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25277099 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of microRNA and mRNA expression signatures in cancer.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015 Oct;36(10):1200-11. doi: 10.1038/aps.2015.67. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015. PMID: 26299954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-138 is a Prognostic Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer and Promotes Tumorigenesis via TUSC2 repression.Sci Rep. 2019 Sep 3;9(1):12718. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-49155-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31481748 Free PMC article.
-
miR-3189-3p Mimics Enhance the Effects of S100A4 siRNA on the Inhibition of Proliferation and Migration of Gastric Cancer Cells by Targeting CFL2.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jan 13;19(1):236. doi: 10.3390/ijms19010236. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29342841 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

