The efficiency of Vpx-mediated SAMHD1 antagonism does not correlate with the potency of viral control in HIV-2-infected individuals
- PMID: 23497283
- PMCID: PMC3599662
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-4690-10-27
The efficiency of Vpx-mediated SAMHD1 antagonism does not correlate with the potency of viral control in HIV-2-infected individuals
Abstract
Background: The presence of a vpx gene distinguishes HIV-2 from HIV-1, the main causative agent of AIDS. Vpx degrades the restriction factor SAMHD1 to boost HIV-2 infection of macrophages and dendritic cells and it has been suggested that the activation of antiviral innate immune responses after Vpx-dependent infection of myeloid cells may explain why most HIV-2-infected individuals efficiently control viral replication and become long-term survivors. However, the role of Vpx-mediated SAMHD1 antagonism in the virological and clinical outcome of HIV-2 infection remained to be investigated.
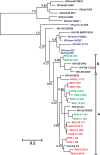
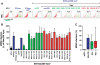
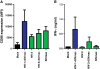
Results: Here, we analyzed the anti-SAMHD1 activity of vpx alleles derived from seven viremic and four long-term aviremic HIV-2-infected individuals. We found that effective Vpx-mediated SAMHD1 degradation and enhancement of myeloid cell infection was preserved in most HIV-2-infected individuals including all seven that failed to control the virus and developed AIDS. The only exception were vpx alleles from an aviremic individual that predicted a M68K change in a highly conserved nuclear localization signal which disrupted the ability of Vpx to counteract SAMHD1. We also found that HIV-2 is less effective than HIV-1 in inducing innate immune activation in dendritic cells.
Conclusions: Effective immune control of viral replication in HIV-2-infected individuals is not associated with increased Vpx-mediated degradation of SAMHD1.
Figures


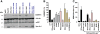
References
-
- Rice GI, Bond J, Asipu A, Brunette RL, Manfield IW, Carr IM, Fuller JC, Jackson RM, Lamb T, Briggs TA, Ali M, Gornall H, Couthard LR, Aeby A, Attard-Montalto SP, Bertini E, Bodemer C, Brockmann K, Brueton LA, Corry PC, Desguerre I, Fazzi E, Cazorla AG, Gener B, Hamel BC, Heiberg A, Hunter M, van der Knaap MS, Kumar R, Lagae L, Landrieu PG, Lourenco CM, Marom D, McDermott MF, van der Merwe W, Orcesi S, Prendiville JS, Rasmussen M, Shalev SA, Soler DM, Shinawi M, Spiegel R, Tan TY, Vanderver A, Wakeling EL, Wassmer E, Whittaker E, Lebon P, Stetson DB, Bonthron DT, Crow YJ. Mutations involved in Aicardi-Goutières syndrome implicate SAMHD1 as regulator of the innate immune response. Nat Genet. 2009;41:829–832. doi: 10.1038/ng.373. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berger A, Sommer AF, Zwarg J, Hamdorf M, Welzel K, Esly N, Panitz S, Reuter A, Ramos I, Jatiani A, Mulder LC, Fernandez-Sesma A, Rutsch F, Simon V, König R, Flory E. SAMHD1-deficient CD14+ cells from individuals with Aicardi-Goutières syndrome are highly susceptible to HIV-1 infection. PLoS Pathog. 2011;7:e1002425. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002425. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Goldstone DC, Ennis-Adeniran V, Hedden JJ, Groom HC, Rice GI, Christodoulou E, Walker PA, Kelly G, Haire LF, Yap MW, de Carvalho LP, Stoye JP, Crow YJ, Taylor IA, Webb M. HIV-1 restriction factor SAMHD1 is a deoxynucleoside triphosphate triphosphohydrolase. Nature. 2011;480:379–382. doi: 10.1038/nature10623. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

