Low expression of PTK6/Brk predicts poor prognosis in patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 23497344
- PMCID: PMC3599503
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-11-59
Low expression of PTK6/Brk predicts poor prognosis in patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Protein tyrosine kinase 6 (PTK6), also known as breast tumor kinase (Brk), was a nonreceptor tyrosine kinase containing SH3, SH2, and tyrosine kinase catalytic domains. The deregulated expression of PTK6 was observed in various human cancers. However, little was known about PTK6 expression and its clinicopathological significance in human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC).
Materials: PTK6 expression was evaluated in 7 pairs of surgically resectable laryngeal tissues by Western blotting and in 13 pairs of surgically resectable laryngeal tissues by reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR). Using immunohistochemistry, we performed a retrospective study of the PTK6 expression levels on 134 archival LSCC paraffin-embedded samples. Prognostic outcomes correlated with PTK6 were examined using Kaplan-Meier analysis and Cox proportional hazards model.
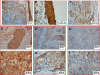
Results: The PTK6 expression level was lower in LSCC tissues than in the adjacent noncancerous epithelial laryngeal tissues by Western blots and RT-PCR. By immunohistochemical analysis, we observed high expression of PTK6 in 25 of 76 (32.9%) adjacent noncancerous epithelial laryngeal tissues and in 39 of 134 (29.1%) of LSCC, respectively. Multivariate analysis demonstrated that pN status and the expression level of PTK6 (P < 0.05) were independent and significant prognostic factors. In the primary LSCC category, median DFS (disease free survival) of high, medium and low PTK6 expression patients were 88.5 months ,74.5 months and 49.0 months (log-rank test, P = 0.002); median OS (overall survival) of high, medium and low PTK6 expression patients were 88.5 months ,76.3 months and 65.7 months (log-rank test, P = 0.002). Reduced cytoplasmic PTK6 expression in LSCC was significantly associated with late pN status (P =0.005, r = 0.27), advanced pTNM stages (III and IV) (P =0.027, r = 0.147), and poor differentiated LSCC (P <0.0001, r = 0.486). In adjacent paracancerous laryngeal epithelial samples, median DFS of high, medium and low PTK6 expression patients were 92.6 months ,75.6 months and 48.5 months (log-rank test, P = 0.020); median OS of high, medium and low PTK6 expression patients were 92.9 months ,78.9 months and 74.6 months (log-rank test, P = 0.042).
Conclusion: The present findings indicated that cytoplasmic PTK6 expression is a potential prognostic factor for survival in LSCC patients. High expression of PTK6 was associated with favorable OS and DFS in LSCC patients.
Figures


References
-
- Mitchell PJ, Barker KT, Martindale JE, Kamalati T, Lowe PN, Page MJ, Gusterson BA, Crompton MR. Cloning and characterization of cDNAs encoding a novel non-receptor tyrosine kinase, BRK, expressed in human breast tumors. Oncogene. 1994;9(8):2383–2390. - PubMed
-
- Zhang P, Ostrander JH, Faivre EJ, Olsen A, Fitzsimmons D, Lange CA. Regulated association of protein kinase B/Akt with breast tumor kinase. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:1982–1991. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

