Measurement of cystatin C functional activity in the cerebrospinal fluid of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and control subjects
- PMID: 23497730
- PMCID: PMC3610126
- DOI: 10.1186/2045-8118-10-15
Measurement of cystatin C functional activity in the cerebrospinal fluid of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and control subjects
Abstract
Background: Cystatin C is a constitutively expressed and abundant cysteine protease inhibitor within the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Recent studies have reported a significant reduction in cystatin C concentration in the CSF of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and several other neurodegenerative diseases, relative to healthy controls. Cystatin C can exhibit both neuroprotective and neurotoxic properties, suggesting that altered CSF cystatin C concentrations could potentially impact the pathogenesis or progression of these disorders. However, it is unclear if alterations in cystatin C concentration result in physiologically relevant differences in its functional activity within the CSF. Measurements of the cysteine protease inhibitory activity of cystatin C within the CSF have not been reported, and the relationship between CSF cystatin C concentration and activity levels in different disease contexts has not been investigated.
Methods: We used a papain inhibition assay to evaluate the total cystatin C activity in CSF samples from 23 ALS patients, 23 healthy controls, and 23 neurological disease controls. Cystatin C concentrations in these samples were previously measured by ELISA. Correlations between cystatin C concentration and activity were assessed with nonparametric statistics. Activity ratios were compared among diagnostic groups using both one-way ANOVA and repeated measures statistics.
Results: Total cystatin C activity was found to be directly proportional to its protein concentration in all subjects, and cystatin C activity was not altered in ALS patients. In addition, our data suggest that cystatin C is the predominant cysteine protease inhibitor in human CSF.
Conclusions: Our data demonstrate the successful measurement of the functional activity of cystatin C in the CSF, and show that total cystatin C activity can be inferred from its total protein concentration. Our results also suggest that cystatin C is the major cysteine protease inhibitor in human CSF and altered CSF cystatin C concentration may play a role in the pathobiology of ALS and other neurological diseases.
Figures

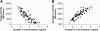
References
-
- Abrahamson M, Barrett AJ, Salvesen G, Grubb A. Isolation of six cysteine proteinase inhibitors from human urine. Their physicochemical and enzyme kinetic properties and concentrations in biological fluids. J Biol Chem. 1986;261:11282–11289. - PubMed
-
- George PM, Sheat JM. Cystatin C quantification in CSF. Clin Chem. 1989;35:179–180. - PubMed
-
- Kato T, Heike T, Okawa K, Haruyama M, Shiraishi K, Yoshimoto M, Nagato M, Shibata M, Kumada T, Yamanaka Y, Hattori H, Nakahata T. A neurosphere-derived factor, cystatin C, supports differentiation of ES cells into neural stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:6019–6024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0509789103. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ranganathan S, Williams E, Ganchev P, Gopalakrishnan V, Lacomis D, Urbinelli L, Newhall K, Cudkowicz ME, Brown RH Jr, Bowser R. Proteomic profiling of cerebrospinal fluid identifies biomarkers for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurochem. 2005;95:1461–1471. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03478.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

