DNA-methylation effect on cotranscriptional splicing is dependent on GC architecture of the exon-intron structure
- PMID: 23502848
- PMCID: PMC3638135
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.143503.112
DNA-methylation effect on cotranscriptional splicing is dependent on GC architecture of the exon-intron structure
Abstract
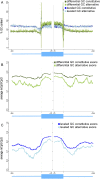
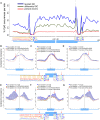
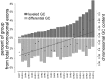
DNA methylation is known to regulate transcription and was recently found to be involved in exon recognition via cotranscriptional splicing. We recently observed that exon-intron architectures can be grouped into two classes: one with higher GC content in exons compared to the flanking introns, and the other with similar GC content in exons and introns. The first group has higher nucleosome occupancy on exons than introns, whereas the second group exhibits weak nucleosome marking of exons, suggesting another type of epigenetic marker distinguishes exons from introns when GC content is similar. We find different and specific patterns of DNA methylation in each of the GC architectures; yet in both groups, DNA methylation clearly marks the exons. Exons of the leveled GC architecture exhibit a significantly stronger DNA methylation signal in relation to their flanking introns compared to exons of the differential GC architecture. This is accentuated by a reduction of the DNA methylation level in the intronic sequences in proximity to the splice sites and shows that different epigenetic modifications mark the location of exons already at the DNA level. Also, lower levels of methylated CpGs on alternative exons can successfully distinguish alternative exons from constitutive ones. Three positions at the splice sites show high CpG abundance and accompany elevated nucleosome occupancy in a leveled GC architecture. Overall, these results suggest that DNA methylation affects exon recognition and is influenced by the GC architecture of the exon and flanking introns.
Figures

References
-
- Amit M, Donyo M, Hollander D, Goren A, Kim E, Gelfman S, Lev-Maor G, Burstein D, Schwartz S, Postolsky B 2012. Differential GC content between exons and introns establishes distinct strategies of splice-site recognition. Cell Rep 1: 543–556 - PubMed
-
- Anastasiadou C, Malousi A, Maglaveras N, Kouidou S 2011. Human epigenome data reveal increased CpG methylation in alternatively spliced sites and putative exonic splicing enhancers. DNA Cell Biol 30: 267–275 - PubMed
-
- Batsché E, Yaniv M, Muchardt C 2006. The human SWI/SNF subunit Brm is a regulator of alternative splicing. Nat Struct Mol Biol 13: 22–29 - PubMed
-
- Bernardi G, Olofsson B, Filipski J, Zerial M, Salinas J, Cuny G, Meunier-Rotival M, Rodier F 1985. The mosaic genome of warm-blooded vertebrates. Science 228: 953–958 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
