Coupling deep transcriptome analysis with untargeted metabolic profiling in Ophiorrhiza pumila to further the understanding of the biosynthesis of the anti-cancer alkaloid camptothecin and anthraquinones
- PMID: 23503598
- PMCID: PMC3653139
- DOI: 10.1093/pcp/pct040
Coupling deep transcriptome analysis with untargeted metabolic profiling in Ophiorrhiza pumila to further the understanding of the biosynthesis of the anti-cancer alkaloid camptothecin and anthraquinones
Abstract
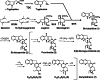
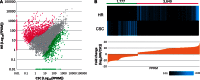
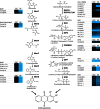
The Rubiaceae species, Ophiorrhiza pumila, accumulates camptothecin, an anti-cancer alkaloid with a potent DNA topoisomerase I inhibitory activity, as well as anthraquinones that are derived from the combination of the isochorismate and hemiterpenoid pathways. The biosynthesis of these secondary products is active in O. pumila hairy roots yet very low in cell suspension culture. Deep transcriptome analysis was conducted in O. pumila hairy roots and cell suspension cultures using the Illumina platform, yielding a total of 2 Gb of sequence for each sample. We generated a hybrid transcriptome assembly of O. pumila using the Illumina-derived short read sequences and conventional Sanger-derived expressed sequence tag clones derived from a full-length cDNA library constructed using RNA from hairy roots. Among 35,608 non-redundant unigenes, 3,649 were preferentially expressed in hairy roots compared with cell suspension culture. Candidate genes involved in the biosynthetic pathway for the monoterpenoid indole alkaloid camptothecin were identified; specifically, genes involved in post-strictosamide biosynthetic events and genes involved in the biosynthesis of anthraquinones and chlorogenic acid. Untargeted metabolomic analysis by Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry (FT-ICR-MS) indicated that most of the proposed intermediates in the camptothecin biosynthetic pathway accumulated in hairy roots in a preferential manner compared with cell suspension culture. In addition, a number of anthraquinones and chlorogenic acid preferentially accumulated in hairy roots compared with cell suspension culture. These results suggest that deep transcriptome and metabolome data sets can facilitate the identification of genes and intermediates involved in the biosynthesis of secondary products including camptothecin in O. pumila.
Keywords: Anthraquinone; Camptothecin; Hairy root; Metabolome; Ophiorrhiza pumila; Transcriptome.
Figures
References
-
- Afendi FM, Okada T, Yamazaki M, Hirai-Morita A, Nakamura Y, Nakamura K, et al. KNApSAcK family databases: integrated metabolite–plant species databases for multifaceted plant research. Plant Cell Physiol. 2012;53:e1. - PubMed
-
- Aharoni A, Ric de Vos CH, Verhoeven HA, Maliepaard CA, Kruppa G, Bino R, et al. Nontargeted metabolome analysis by use of Fourier transform ion cyclotron mass spectrometry. OMICS. 2002;6:217–234. - PubMed
-
- Aimi N, Hoshino H, Nishimura M, Sakai S-i, Haginiwa J. Chaboside, first natural glycocamptothecin found from Ophiorrhiza pumila. Tetrahedron Lett. 1990;31:5169–5172.
-
- Aimi N, Nishimura M, Miwa A, Hoshino H, Sakai S-i, Haginiwa J. Pumiloside and deoxypumiloside; plausible intermediates of camptothecin biosynthesis. Tetrahedron Lett. 1989;30:4991–4994.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

