RfaH promotes the ability of the avian pathogenic Escherichia coli O2 strain E058 to cause avian colibacillosis
- PMID: 23504015
- PMCID: PMC3676060
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.02074-12
RfaH promotes the ability of the avian pathogenic Escherichia coli O2 strain E058 to cause avian colibacillosis
Abstract
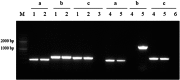
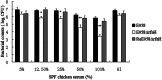
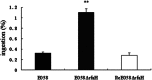
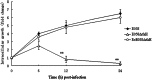
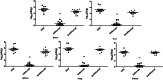
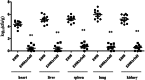
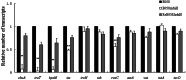
Avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) infection causes avian colibacillosis, which refers to any localized or systemic infection, such as acute fatal septicemia or subacute pericarditis and airsacculitis. The RfaH transcriptional regulator in E. coli is known to regulate a number of phenotypic traits. The direct effect of RfaH on the virulence of APEC has not been investigated yet. Our results showed that the inactivation of rfaH significantly decreased the virulence of APEC E058. The attenuation was assessed by in vivo and in vitro assays, including chicken infection assays, an ingestion and intracellular survival assay, and a bactericidal assay with serum complement. The virulence phenotype was restored to resemble that of the wild type by complementation of the rfaH gene in trans. The results of the quantitative real-time reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis and animal system infection experiments indicated that the deletion of rfaH correlated with decreased virulence of the APEC E058 strain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RstA is required for the virulence of an avian pathogenic Escherichia coli O2 strain E058.Infect Genet Evol. 2015 Jan;29:180-8. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2014.11.022. Epub 2014 Nov 26. Infect Genet Evol. 2015. PMID: 25461694
-
SodA Contributes to the Virulence of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli O2 Strain E058 in Experimentally Infected Chickens.J Bacteriol. 2019 Feb 25;201(6):e00625-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00625-18. Print 2019 Mar 15. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 30602490 Free PMC article.
-
The transfer-messenger RNA-small protein B system plays a role in avian pathogenic Escherichia coli pathogenicity.J Bacteriol. 2013 Nov;195(22):5064-71. doi: 10.1128/JB.00628-13. Epub 2013 Sep 6. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 24013628 Free PMC article.
-
[Avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC)].Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2003 Sep-Oct;116(9-10):381-95. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2003. PMID: 14526468 Review. German.
-
Avian colibacillosis: still many black holes.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2015 Aug;362(15):fnv118. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnv118. Epub 2015 Jul 23. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2015. PMID: 26204893 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel small molecules affecting cell membrane as potential therapeutics for avian pathogenic Escherichia coli.Sci Rep. 2018 Oct 17;8(1):15329. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-33587-5. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30333507 Free PMC article.
-
IbeR facilitates stress-resistance, invasion and pathogenicity of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 13;10(3):e0119698. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119698. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25768126 Free PMC article.
-
Novel small molecule modulators of quorum sensing in avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC).Virulence. 2018;9(1):1640-1657. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2018.1528844. Virulence. 2018. PMID: 30270715 Free PMC article.
-
DotU expression is highly induced during in vivo infection and responsible for virulence and Hcp1 secretion in avian pathogenic Escherichia coli.Front Microbiol. 2014 Nov 7;5:588. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00588. eCollection 2014. Front Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25426107 Free PMC article.
-
Phage Resistance Accompanies Reduced Fitness of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli in the Urinary Environment.mSphere. 2022 Aug 31;7(4):e0034522. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00345-22. Epub 2022 Aug 3. mSphere. 2022. PMID: 35920561 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Russo TA, Johnson JR. 2000. Proposal for a new inclusive designation for extraintestinal pathogenic isolates of Escherichia coli: ExPEC. J. Infect. Dis. 181:1753–1754 - PubMed
-
- Mokady D, Gophna U, Ron EZ. 2005. Virulence factors of septicemic Escherichia coli strains. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 295:455–462 - PubMed
-
- Zhao L, Gao S, Huan H, Xu X, Zhu X, Yang W, Gao Q, Liu X. 2009. Comparison of virulence factors and expression of specific genes between uropathogenic Escherichia coli and avian pathogenic E. coli in a murine urinary tract infection model and a chicken challenge model. Microbiology 155:1634–1644 - PubMed
-
- Cheville NF, Arp LH. 1978. Comparative pathologic findings of Escherichia coli infection in birds. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 173:584–587 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

