Role of RNF4 in the ubiquitination of Rta of Epstein-Barr virus
- PMID: 23504328
- PMCID: PMC3642330
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.413393
Role of RNF4 in the ubiquitination of Rta of Epstein-Barr virus
Abstract
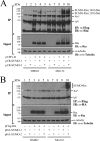
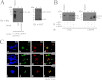
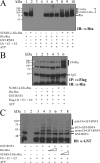
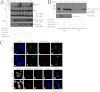
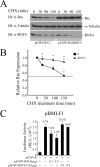
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) encodes a transcription factor, Rta, which is required to activate the transcription of EBV lytic genes. This study demonstrates that treating P3HR1 cells with a proteasome inhibitor, MG132, causes the accumulation of SUMO-Rta and promotes the expression of EA-D. GST pulldown and coimmunoprecipitation studies reveal that RNF4, a RING-domain-containing ubiquitin E3 ligase, interacts with Rta. RNF4 also targets SUMO-2-conjugated Rta and promotes its ubiquitination in vitro. Additionally, SUMO interaction motifs in RNF4 are important to the ubiquitination of Rta because the RNF4 mutant with a mutation at the motifs eliminates ubiquitination. The mutation of four lysine residues on Rta that abrogated SUMO-3 conjugation to Rta also decreases the enhancement of the ubiquitination of Rta by RNF4. This finding demonstrates that RNF4 is a SUMO-targeted ubiquitin E3 ligase of Rta. Finally, knockdown of RNF4 enhances the expression of Rta and EA-D, subsequently promoting EBV lytic replication and virions production. Results of this study significantly contribute to efforts to elucidate a SUMO-targeted ubiquitin E3 ligase that regulates Rta ubiquitination to influence the lytic development of EBV.
Keywords: DNA Viruses; E3 Ubiquitin Ligase; Epstein-Barr Virus; Protein Degradation; RNF4; Rta; Sumoylation; Ubiquitination.
Figures



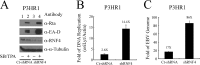
Similar articles
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus K-Rta exhibits SUMO-targeting ubiquitin ligase (STUbL) like activity and is essential for viral reactivation.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(8):e1003506. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003506. Epub 2013 Aug 22. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23990779 Free PMC article.
-
The Epstein-Barr virus miR-BHRF1-1 targets RNF4 during productive infection to promote the accumulation of SUMO conjugates and the release of infectious virus.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Apr 17;13(4):e1006338. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006338. eCollection 2017 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28414785 Free PMC article.
-
Rta is an Epstein-Barr virus tegument protein that improves the stability of capsid protein BORF1.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Mar 12;523(3):773-779. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.01.017. Epub 2020 Jan 14. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 31948747
-
Protein Degradation by Gammaherpesvirus RTAs: More Than Just Viral Transactivators.Viruses. 2023 Mar 11;15(3):730. doi: 10.3390/v15030730. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36992439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
E3 Ubiquitin Ligases in Gammaherpesviruses and HIV: A Review of Virus Adaptation and Exploitation.Viruses. 2023 Sep 15;15(9):1935. doi: 10.3390/v15091935. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37766341 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Functional diversity: update of the posttranslational modification of Epstein-Barr virus coding proteins.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Nov 14;79(12):590. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04561-2. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 36376593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding Epstein-Barr Virus Life Cycle with Proteomics: A Temporal Analysis of Ubiquitination During Virus Reactivation.OMICS. 2017 Jan;21(1):27-37. doi: 10.1089/omi.2016.0158. OMICS. 2017. PMID: 28271981 Free PMC article.
-
Using glycyrrhizic acid to target sumoylation processes during Epstein-Barr virus latency.PLoS One. 2019 May 24;14(5):e0217578. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217578. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31125383 Free PMC article.
-
Less Cytotoxic Protoflavones as Antiviral Agents: Protoapigenone 1'-O-isopropyl ether Shows Improved Selectivity Against the Epstein-Barr Virus Lytic Cycle.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 12;20(24):6269. doi: 10.3390/ijms20246269. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31842358 Free PMC article.
-
Arsenic trioxide inhibits EBV reactivation and promotes cell death in EBV-positive lymphoma cells.Virol J. 2017 Jun 21;14(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s12985-017-0784-7. Virol J. 2017. PMID: 28637474 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pickart C. M., Fushman D. (2004) Polyubiquitin chains. Polymeric protein signals. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 8, 610–616 - PubMed
-
- Chau V., Tobias J. W., Bachmair A., Marriott D., Ecker D. J., Gonda D. K., Varshavsky A. (1989) A multiubiquitin chain is confined to specific lysine in a targeted short-lived protein. Science 243, 1576–1583 - PubMed
-
- Komander D. (2009) The emerging complexity of protein ubiquitination. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 37, 937–953 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

