Technologies for investigating the physiological barriers to efficient lipid nanoparticle-siRNA delivery
- PMID: 23504369
- PMCID: PMC3715328
- DOI: 10.1369/0022155413484152
Technologies for investigating the physiological barriers to efficient lipid nanoparticle-siRNA delivery
Abstract
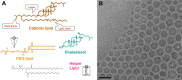
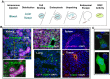
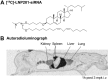
Small interfering RNA (siRNA) therapeutics have advanced from bench to clinical trials in recent years, along with new tools developed to enable detection of siRNA delivered at the organ, cell, and subcellular levels. Preclinical models of siRNA delivery have benefitted from methodologies such as stem-loop quantitative polymerase chain reaction, histological in situ immunofluorescent staining, endosomal escape assay, and RNA-induced silencing complex loading assay. These technologies have accelerated the detection and optimization of siRNA platforms to overcome the challenges associated with delivering therapeutic oligonucleotides to the cytosol of specific target cells. This review focuses on the methodologies and their application in the biodistribution of siRNA delivered by lipid nanoparticles.
Keywords: LNP; QWBA; RISC; biodistribution; delivery; endosomal escape; immunofluorescence staining; intravital imaging; lipid nanoparticle; siRNA; stem-loop PCR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Akita H, Kogure K, Moriguchi R, Nakamura Y, Higashi T, Nakamura T, Serada S, Fujimoto M, Naka T, Futaki S, et al. 2010. Nanoparticles for ex vivo siRNA delivery to dendritic cells for cancer vaccines: programmed endosomal escape and dissociation. J Control Release. 143:311–317 - PubMed
-
- Aroeti B, Henis YI. 1991. Accumulation of Sendai virus glycoproteins in cell-cell contact regions and its role in cell fusion. J Biol Chem. 266:15845–15849 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

