Human Mas-related G protein-coupled receptors-X1 induce chemokine receptor 2 expression in rat dorsal root ganglia neurons and release of chemokine ligand 2 from the human LAD-2 mast cell line
- PMID: 23505557
- PMCID: PMC3591377
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058756
Human Mas-related G protein-coupled receptors-X1 induce chemokine receptor 2 expression in rat dorsal root ganglia neurons and release of chemokine ligand 2 from the human LAD-2 mast cell line
Abstract
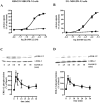
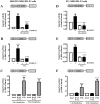
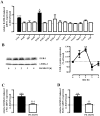
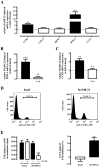
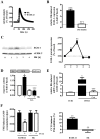
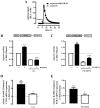
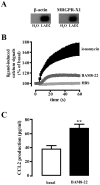
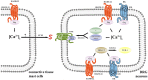
Primate-specific Mas-related G protein-coupled receptors-X1 (MRGPR-X1) are highly enriched in dorsal root ganglia (DRG) neurons and induce acute pain. Herein, we analyzed effects of MRGPR-X1 on serum response factors (SRF) or nuclear factors of activated T cells (NFAT), which control expression of various markers of chronic pain. Using HEK293, DRG neuron-derived F11 cells and cultured rat DRG neurons recombinantly expressing human MRGPR-X1, we found activation of a SRF reporter gene construct and induction of the early growth response protein-1 via extracellular signal-regulated kinases-1/2 known to play a significant role in the development of inflammatory pain. Furthermore, we observed MRGPR-X1-induced up-regulation of the chemokine receptor 2 (CCR2) via NFAT, which is considered as a key event in the onset of neuropathic pain and, so far, has not yet been described for any endogenous neuropeptide. Up-regulation of CCR2 is often associated with increased release of its endogenous agonist chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2). We also found MRGPR-X1-promoted release of CCL2 in a human connective tissue mast cell line endogenously expressing MRGPR-X1. Thus, we provide first evidence to suggest that MRGPR-X1 induce expression of chronic pain markers in DRG neurons and propose a so far unidentified signaling circuit that enhances chemokine signaling by acting on two distinct yet functionally co-operating cell types. Given the important role of chemokine signaling in pain chronification, we propose that interruption of this signaling circuit might be a promising new strategy to alleviate chemokine-promoted pain.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human sensory neuron-specific Mas-related G protein-coupled receptors-X1 sensitize and directly activate transient receptor potential cation channel V1 via distinct signaling pathways.J Biol Chem. 2012 Nov 30;287(49):40956-71. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.408617. Epub 2012 Oct 16. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23074220 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) mediates upregulation of CCR2 chemokine receptors in dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons: a possible mechanism for activity-dependent transcription in DRG neurons in association with neuropathic pain.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2008 Jan;37(1):170-7. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2007.09.004. Epub 2007 Sep 14. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 17949992 Free PMC article.
-
Morphine activates the E twenty six-like transcription factor-1/serum response factor pathway via extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 in F11 cells derived from dorsal root ganglia neurons.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012 Jul;342(1):41-52. doi: 10.1124/jpet.112.192757. Epub 2012 Mar 27. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012. PMID: 22454534
-
The role of Mrgprs in pain.Neurosci Lett. 2021 Jan 23;744:135544. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2020.135544. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Neurosci Lett. 2021. PMID: 33421487 Review.
-
MAS and its related G protein-coupled receptors, Mrgprs.Pharmacol Rev. 2014 Oct;66(4):1080-105. doi: 10.1124/pr.113.008136. Pharmacol Rev. 2014. PMID: 25244929 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential Local Mechanisms for Exercise-Induced Hypoalgesia in Response to Blood Flow Restriction Training.Cureus. 2023 Aug 9;15(8):e43219. doi: 10.7759/cureus.43219. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37692724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Berbamine Reduces Chloroquine-Induced Itch in Mice through Inhibition of MrgprX1.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 18;23(22):14321. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214321. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430803 Free PMC article.
-
Microinjection of pruritogens in NGF-sensitized human skin.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 2;11(1):21490. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-00935-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34728705 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Roles of the Calcineurin-Nuclear Factor of Activated T-Lymphocytes Pathway in Nervous System Functions and Diseases.J Aging Res. 2016;2016:5081021. doi: 10.1155/2016/5081021. Epub 2016 Aug 15. J Aging Res. 2016. PMID: 27597899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wnt5a/β-catenin signaling drives calcium-induced differentiation of human primary keratinocytes.J Invest Dermatol. 2014 Aug;134(8):2183-2191. doi: 10.1038/jid.2014.149. Epub 2014 Mar 21. J Invest Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 24658506
References
-
- Lembo PM, Grazzini E, Groblewski T, O'Donnell D, Roy MO, et al. (2002) Proenkephalin A gene products activate a new family of sensory neuron – specific GPCRs. Nat Neurosci 5: 201–209. - PubMed
-
- Dong X, Han S, Zylka MJ, Simon MI, Anderson DJ (2001) A diverse family of GPCRs expressed in specific subsets of nociceptive sensory neurons. Cell 106: 619–632. - PubMed
-
- Tatemoto K, Nozaki Y, Tsuda R, Konno S, Tomura K, et al. (2006) Immunoglobulin E-independent activation of mast cell is mediated by Mrg receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 349: 1322–1328. - PubMed
-
- Breit A, Gagnidze K, Devi LA, Lagace M, Bouvier M (2006) Simultaneous activation of the delta opioid receptor (deltaOR)/sensory neuron-specific receptor-4 (SNSR-4) hetero-oligomer by the mixed bivalent agonist bovine adrenal medulla peptide 22 activates SNSR-4 but inhibits deltaOR signaling. Mol Pharmacol 70: 686–696. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

