'TXT2BFiT' a mobile phone-based healthy lifestyle program for preventing unhealthy weight gain in young adults: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 23506013
- PMCID: PMC3610110
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-14-75
'TXT2BFiT' a mobile phone-based healthy lifestyle program for preventing unhealthy weight gain in young adults: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Despite international efforts to arrest increasing rates of overweight and obesity, many population strategies have neglected young adults as a target group. Young adults are at high risk for unhealthy weight gain which tends to persist throughout adulthood with associated chronic disease health risks.
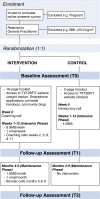
Methods/design: TXT2BFiT is a nine month two-arm parallel-group randomized controlled trial aimed at improving weight management and weight-related dietary and physical activity behaviors among young adults. Participants are recruited via general practice (primary medical care) clinics in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. All participants receive a mailed resource outlining national physical activity and dietary guidelines and access to the study website. Additional resources accessible to the intervention arm via the study website include Smartphone mobile applications, printable handouts, an interactive healthy weight tracker chart, and a community blog. The study consists of two phases: (1) Intensive phase (weeks 1 to 12): the control arm receives four short message service (SMS) text messages; the intervention arm receives eight SMS messages/week tailored to their baseline stage-of-change, one Email/week, and personalized coaching calls during weeks 0, 2, 5, 8, and 11; and (2) Maintenance phase (weeks 14 to 36): the intervention arm receives one SMS message/month, one Email/month and booster coaching calls during months 5 and 8. A sample of N = 354 (177 per arm) is required to detect differences in primary outcomes: body weight (kg) and body mass index (kg/m2), and secondary outcomes: physical activity, sitting time, intake of specific foods, beverages and nutrients, stage-of-change, self-efficacy and participant well-being, at three and nine months. Program reach, costs, implementation and participant engagement will also be assessed.
Discussion: This mobile phone based program addresses an important gap in obesity prevention efforts to date. The method of intervention delivery is via platforms that are highly accessible and appropriate for this population group. If effective, further translational research will be required to assess how this program might operate in the broader community.
Trial registration: Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry ACTRN12612000924853.
Figures
References
-
- Finucane MM, Stevens GA, Cowan MJ, Danaei G, Lin JK, Paciorek CJ, Singh GM, Gutierrez HR, Lu Y, Bahalim AN. et al.National, regional, and global trends in body-mass index since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 960 country-years and 9·1 million participants. Lancet. 2011;377:557–567. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62037-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous