Dopamine D3 receptors regulate reconsolidation of cocaine memory
- PMID: 23506736
- PMCID: PMC3646898
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.03.005
Dopamine D3 receptors regulate reconsolidation of cocaine memory
Abstract
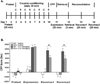
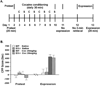
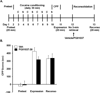
Memories of learned associations between the rewarding properties of drugs of abuse and environmental cues contribute to craving and relapse in humans. Disruption of reconsolidation dampens or even erases previous memories. Dopamine (DA) mediates the acquisition of reward memory and drugs of abuse can pathologically change related neuronal circuits in the mesolimbic DA system. Previous studies showed that DA D3 receptors are involved in cocaine-conditioned place preference (CPP) and reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior. However, the role of D3 receptors in reconsolidation of cocaine-induced reward memory remains unclear. In the present study, we combined genetic and pharmacological approaches to investigate the role of D3 receptors in reconsolidation of cocaine-induced CPP. We found that the mutation of the D3 receptor gene weakened reconsolidation of cocaine-induced CPP in mice triggered by a 3-min (min) retrieval. Furthermore, treatment of a selective D3 receptor antagonist PG01037 immediately following the 3-min retrieval disrupted reconsolidation of cocaine-induced CPP in wild-type mice and such disruption remained at least 1 week after the 3-min retrieval. These results suggest that D3 receptors play a key role in reconsolidation of cocaine-induced CPP in mice, and that pharmacological blockade of these receptors may be therapeutic for the treatment of cocaine craving and relapse in clinical settings.
Copyright © 2013 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dopamine D1 and D3 receptors mediate reconsolidation of cocaine memories in mouse models of drug self-administration.Neuroscience. 2014 Oct 10;278:154-64. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.08.008. Epub 2014 Aug 20. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 25149631 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of dopamine D3 receptors inhibits reward-related learning induced by cocaine.Neuroscience. 2011 Mar 10;176:152-61. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.12.008. Epub 2010 Dec 16. Neuroscience. 2011. PMID: 21168475 Free PMC article.
-
β1-Adrenoceptor in the Central Amygdala Is Required for Unconditioned Stimulus-Induced Drug Memory Reconsolidation.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018 Mar 1;21(3):267-280. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyx104. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29216351 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating reconsolidation and extinction to regulate drug reward memory.Eur J Neurosci. 2019 Aug;50(3):2503-2512. doi: 10.1111/ejn.14072. Epub 2018 Aug 16. Eur J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30113098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting extinction and reconsolidation mechanisms to combat the impact of drug cues on addiction.Neuropharmacology. 2009;56 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):186-95. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.07.027. Epub 2008 Jul 30. Neuropharmacology. 2009. PMID: 18708077 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-edited skin epidermal stem cells protect mice from cocaine-seeking behaviour and cocaine overdose.Nat Biomed Eng. 2019 Feb;3(2):105-113. doi: 10.1038/s41551-018-0293-z. Epub 2018 Sep 17. Nat Biomed Eng. 2019. PMID: 30899600 Free PMC article.
-
Amygdala Dopamine Receptors Are Required for the Destabilization of a Reconsolidating Appetitive Memory.eNeuro. 2015 Mar 6;2(1):ENEURO.0024-14.2015. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0024-14.2015. eCollection 2015 Jan-Feb. eNeuro. 2015. PMID: 26464966 Free PMC article.
-
Windows of change: Revisiting temporal and molecular dynamics of memory reconsolidation and persistence.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2025 Jul;174:106198. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2025.106198. Epub 2025 May 10. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2025. PMID: 40354954 Review.
-
Dopamine D1 and D3 receptors mediate reconsolidation of cocaine memories in mouse models of drug self-administration.Neuroscience. 2014 Oct 10;278:154-64. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.08.008. Epub 2014 Aug 20. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 25149631 Free PMC article.
-
Further characterization of quinpirole-elicited yawning as a model of dopamine D3 receptor activation in male and female monkeys.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014 Aug;350(2):205-11. doi: 10.1124/jpet.114.214833. Epub 2014 May 29. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014. PMID: 24876234 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beaulieu JM, Gainetdinov RR. The physiology, signaling, and pharmacology of dopamine receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 2011;63:182–217. - PubMed
-
- Boileau I, Payer D, Houle S, Behzadi A, Rusjan PM, Tong J, Wilkins D, Selby P, George TP, Zack M, Furukawa Y, McCluskey T, Wilson AA, Kish SJ. Higher binding of the dopamine D3 receptor-preferring ligand [11C]-(+)-propyl-hexahydro-naphtho-oxazin in methamphetamine polydrug users: a positron emission tomography study. J Neurosci. 2012;32:1353–1359. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cervo L, Cocco A, Petrella C, Heidbreder CA. Selective antagonism at dopamine D3 receptors attenuates cocaine-seeking behaviour in the rat. Int J Neuropsychopharm. 2007;10:167–181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

